What Targets Somatic Hypermutation to the Immunoglobulin Loci?
- PMID: 31770070
- PMCID: PMC7247024
- DOI: 10.1089/vim.2019.0149
What Targets Somatic Hypermutation to the Immunoglobulin Loci?
Abstract
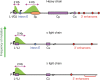
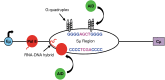
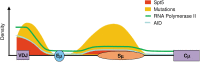
One of the most profound enigmas in B cell biology is how activation-induced deaminase (AID) is targeted to a very small region of DNA in the immunoglobulin loci. Two specific regions are singled out: the variable region of 2 kb that contains rearranged genes on the heavy, κ light, and λ light chain loci, and the switch region of ∼4 kb that contains an extensive stretch of G:C rich DNA on the heavy chain locus. Transcription is required for AID recruitment; however, many genes are also highly transcribed and do not undergo the catastrophic mutagenesis that occurs in variable and switch regions. The DNA sequences of these regions cause RNA polymerase II to accumulate for an extended distance of 2-4 kb. The stalled polymerases then recruit the transcription cofactor Spt5, and AID, which deaminates cytosines to uracils in exposed transcription bubbles. Thus, the immunoglobulin loci are unique in that a favorable combination of DNA sequences and 3' transcription enhancers make them the perfect storm for AID-induced somatic hypermutation.
Keywords: AID; class switch recombination; somatic hypermutation; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spt5 accumulation at variable genes distinguishes somatic hypermutation in germinal center B cells from ex vivo-activated cells.J Exp Med. 2014 Oct 20;211(11):2297-306. doi: 10.1084/jem.20131512. Epub 2014 Oct 6. J Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25288395 Free PMC article.
-
The Chromatin Reader ZMYND8 Regulates Igh Enhancers to Promote Immunoglobulin Class Switch Recombination.Mol Cell. 2018 Nov 15;72(4):636-649.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.042. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30293785 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the immunoglobulin heavy chain class switch recombination mechanism.Adv Immunol. 2007;94:157-214. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(06)94006-1. Adv Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17560275 Review.
-
Transcription elongation factor ELOF1 is required for efficient somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination.Mol Cell. 2025 Apr 3;85(7):1296-1310.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2025.02.007. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Mol Cell. 2025. PMID: 40049160
-
AID targeting in antibody diversity.Adv Immunol. 2011;110:1-26. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387663-8.00005-3. Adv Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21762814 Review.
Cited by
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors of Activation-Induced Deaminase Decrease Class Switch Recombination in B Cells.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021 May 7;4(3):1214-1226. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00064. eCollection 2021 Jun 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 34151211 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of DNA Repair in Immunological Diversity: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Ramifications.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 1;13:834889. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.834889. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35432317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A proposed reverse transcription mechanism for (CAG)n and similar expandable repeats that cause neurological and other diseases.Heliyon. 2020 Feb 26;6(2):e03258. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03258. eCollection 2020 Feb. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32140575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism and regulation of secondary immunoglobulin diversification.Cell Cycle. 2023 Sep;22(18):2070-2087. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2275397. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Cell Cycle. 2023. PMID: 37909747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promoter Proximity Defines Mutation Window for VH and VΚ Genes Rearranged to Different J Genes.J Immunol. 2022 May 1;208(9):2220-2226. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2101002. Epub 2022 Apr 13. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35418469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Betz AG, Milstein C, Gonzalez-Fernandez A, et al. . Elements regulating somatic hypermutation of an immunoglobulin kappa gene: critical role for the intron enhancer/matrix attachment region. Cell 1994;77:239–248 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

