Cross-Talk between Lipoproteins and Inflammation: The Role of Microvesicles
- PMID: 31771128
- PMCID: PMC6947387
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8122059
Cross-Talk between Lipoproteins and Inflammation: The Role of Microvesicles
Abstract
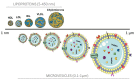
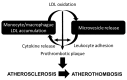
Atherothrombosis is the principal underlying cause of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Microvesicles (MV) are small blebs originated by an outward budding at the cell plasma membranes, which are released in normal conditions. However, MV release is increased in pathophysiologic conditions such as CVD. Low density lipoprotein (LDL) and MV contribute to atherothrombosis onset and progression by promoting inflammation and leukocyte recruitment to injured endothelium, as well as by increasing thrombosis and plaque vulnerability. Moreover, (oxidized)LDL induces MV release and vice-versa, perpetuating endothelium injury leading to CVD progression. Therefore, MV and lipoproteins exhibit common features, which should be considered in the interpretation of their respective roles in the pathophysiology of CVD. Understanding the pathways implicated in this process will aid in developing novel therapeutic approaches against atherothrombosis.
Keywords: LDL cholesterol; atherothrombosis; cardiovascular disease; endothelial cells; inflammation; leukocytes; lipoproteins; microparticles; microvesicles; platelets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Platelet-Derived Microvesicles As Crosstalk Mediators in Atherothrombosis and Future Pharmacology Targets: A Link between Inflammation, Atherosclerosis, and Thrombosis.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Aug 31;7:293. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00293. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27630570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From pathophysiology to targeted therapy for atherothrombosis: a role for the combination of statin and aspirin in secondary prevention.Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Jan;113(1):184-96. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.08.005. Epub 2006 Sep 15. Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17070923 Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in atherothrombosis and cardiovascular disease: Friends and foes.Atherosclerosis. 2021 Aug;330:61-75. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.07.002. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Atherosclerosis. 2021. PMID: 34256307 Review.
-
Liquid Biopsies: Microvesicles in Cardiovascular Disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020 Sep 20;33(9):645-662. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7922. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020. PMID: 31696726 Review.
-
PCSK9 Biology and Its Role in Atherothrombosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 30;22(11):5880. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115880. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34070931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Dynamic and Static Light Scattering for Size and Shape Characterization of Small Extracellular Nanoparticles in Plasma and Ascites of Ovarian Cancer Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 30;22(23):12946. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312946. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884751 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Kidney Transplantation on Accelerated Immunosenescence and Vascular Changes Induced by Chronic Kidney Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Sep 27;8:705159. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.705159. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34646838 Free PMC article.
-
Antiplatelet Effects of PCSK9 Inhibitors in Primary Hypercholesterolemia.Life (Basel). 2021 May 23;11(6):466. doi: 10.3390/life11060466. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34071103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Linking Inflammation, Cancer and Thrombotic Risks.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 17;10:859863. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.859863. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35372327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial Microparticles as Potential Biomarkers in the Assessment of Endothelial Dysfunction in Hypercholesterolemia.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jun 19;58(6):824. doi: 10.3390/medicina58060824. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35744087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Silverman M.G., Ference B.A., Im K., Wiviott S.D., Giugliano R.P., Grundy S.M., Braunwald E., Sabatine M.S. Association Between Lowering LDL-C and Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Among Different Therapeutic Interventions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016;316:1289–1297. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.13985. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zerrad-Saadi A., Therond P., Chantepie S., Couturier M., Rye K.-A., Chapman M.J., Kontush A. HDL3-Mediated Inactivation of LDL-Associated Phospholipid Hydroperoxides Is Determined by the Redox Status of Apolipoprotein A-I and HDL Particle Surface Lipid Rigidity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009;29:2169–2175. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.194555. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

