The Endocannabinoid System in Pediatric Inflammatory and Immune Diseases
- PMID: 31771129
- PMCID: PMC6928713
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20235875
The Endocannabinoid System in Pediatric Inflammatory and Immune Diseases
Erratum in
-
Correction: Argenziano, M., et al. The Endocannabinoid System in Pediatric Inflammatory and Immune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5875.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 15;21(8):2757. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082757. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326655 Free PMC article.
Abstract
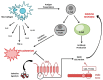
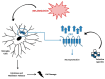
Endocannabinoid system consists of cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid type 2 (CB2) receptors, their endogenous ligands, and the enzymes responsible for their synthesis and degradation. CB2, to a great extent, and CB1, to a lesser extent, are involved in regulating the immune response. They also regulate the inflammatory processes by inhibiting pro-inflammatory mediator release and immune cell proliferation. This review provides an overview on the role of the endocannabinoid system with a major focus on cannabinoid receptors in the pathogenesis and onset of inflammatory and autoimmune pediatric diseases, such as immune thrombocytopenia, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, obesity, neuroinflammatory diseases, and type 1 diabetes mellitus. These disorders have a high social impact and represent a burden for the healthcare system, hence the importance of individuating more innovative and effective treatments. The endocannabinoid system could address this need, representing a possible new diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.
Keywords: CB1 receptor; CB2 receptor; endocannabinoid system; immune regulation; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fride E. The endocannabinoid-CB receptor system: Importance for development and in pediatric disease. Neuro. Endocrinol. Lett. 2004;25:24–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

