Global virus outbreaks: Interferons as 1st responders
- PMID: 31771760
- PMCID: PMC7128104
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2019.101300
Global virus outbreaks: Interferons as 1st responders
Abstract
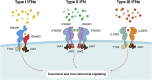
Outbreaks of severe virus infections with the potential to cause global pandemics are increasing. In many instances these outbreaks have been newly emerging (SARS coronavirus), re-emerging (Ebola virus, Zika virus) or zoonotic (avian influenza H5N1) virus infections. In the absence of a targeted vaccine or a pathogen-specific antiviral, broad-spectrum antivirals would function to limit virus spread. Given the direct antiviral effects of type I interferons (IFNs) in inhibiting the replication of both DNA and RNA viruses at different stages of their replicative cycles, and the effects of type I IFNs on activating immune cell populations to clear virus infections, IFNs-α/β present as ideal candidate broad-spectrum antivirals.
Keywords: Antiviral; Immune response; Interferons-α/β.
Crown Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Isaacs A., Lindenmann J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1957;147:258–267. - PubMed
-
- Au W.C., Moore P.A., LaFleur D.W., Tombal B., Pitha P.M. Characterization of the interferon regulatory factor-7 and its potential role in the transcription activation of interferon A genes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:29210–29217. - PubMed
-
- Matsusaka T., Fujikawa K., Nishio Y., Mukaida N., Matsushima K., Kishimoto T., Akira S. Transcription factors NF-IL6 and NF-kappa B synergistically activate transcription of the inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 6 and interleukin 8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1993;90:10193–10197. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

