Differences in cNOS/iNOS Activity during Resistance to Trypanosoma cruzi Infection in 5-Lipoxygenase Knockout Mice
- PMID: 31772504
- PMCID: PMC6854994
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/5091630
Differences in cNOS/iNOS Activity during Resistance to Trypanosoma cruzi Infection in 5-Lipoxygenase Knockout Mice
Abstract
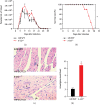
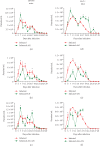
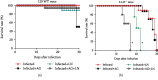
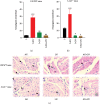
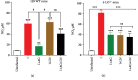
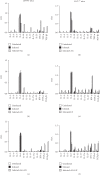
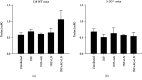
Infection with the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi causes Chagas disease and consequently leads to severe inflammatory heart condition; however, the mechanisms driving this inflammatory response have not been completely elucidated. Nitric oxide (NO) is a key mediator of parasite killing in T. cruzi-infected mice, and previous studies have suggested that leukotrienes (LTs) essentially regulate the NO activity in the heart. We used infected 5-lipoxygenase-deficient mice (5-LO-/-) to explore the participation of nitric oxide synthase isoforms, inducible (iNOS) and constitutive (cNOS), in heart injury, cytokine profile, and oxidative stress during the early stage of T. cruzi infection. Our evidence suggests that the cNOS of the host is involved in the resistance of 5-LO-/- mice during T. cruzi infection. iNOS inhibition generated a remarkable increase in T. cruzi infection in the blood and heart of mice, whereas cNOS inhibition reduced cardiac parasitism (amastigote nests). Furthermore, this inhibition associates with a higher IFN-γ production and lower lipid peroxidation status. These data provide a better understanding about the influence of NO-interfering therapies for the inflammatory response toward T. cruzi infection.
Copyright © 2019 Carolina Panis et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that would prejudice the impartiality of this scientific work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
5-Lipoxygenase plays a role in the control of parasite burden and contributes to oxidative damage of erythrocytes in murine Chagas' disease.Immunol Lett. 2009 Mar 24;123(1):38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2009.02.002. Epub 2009 Feb 14. Immunol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19428550
-
Trypanosoma cruzi: effect of the absence of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO)-derived leukotrienes on levels of cytokines, nitric oxide and iNOS expression in cardiac tissue in the acute phase of infection in mice.Exp Parasitol. 2011 Jan;127(1):58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2010.06.030. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Exp Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 20599987
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase in heart tissue and nitric oxide in serum of Trypanosoma cruzi-infected rhesus monkeys: association with heart injury.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(5):e1644. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001644. Epub 2012 May 8. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012. PMID: 22590660 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of nitric oxide on the immune system during Trypanosoma cruzi infection.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2009 Jul;104 Suppl 1:236-45. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762009000900030. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2009. PMID: 19753479 Review.
-
[Role of cytokines in resistance and pathology in Trypanosoma cruzi infection].Rev Argent Microbiol. 1996 Apr-Jun;28(2):99-109. Rev Argent Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8768488 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Toxoplasma gondii Infection Decreases Intestinal 5-Lipoxygenase Expression, while Exogenous LTB4 Controls Parasite Growth.Infect Immun. 2022 Jul 21;90(7):e0002922. doi: 10.1128/iai.00029-22. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Infect Immun. 2022. PMID: 35658510 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Acid Composition and Metabolism in Leishmania Parasite Species: Potential Biomarkers or Drug Targets for Leishmaniasis?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 28;24(5):4702. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054702. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902138 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chagas C. Nova tripanozomiaze humana: estudos sobre a morfolojia e o ciclo evolutivo do Schizotrypanum cruzi n. gen., n. sp., ajente etiolojico de nova entidade morbida do homem. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz. 1909;1(2):159–218. doi: 10.1590/S0074-02761909000200008. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

