Long-Term Outcomes of Extent of Revascularization in Complex High Risk and Indicated Patients Undergoing Impella-Protected Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Report from the Roma-Verona Registry
- PMID: 31772533
- PMCID: PMC6739781
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/5243913
Long-Term Outcomes of Extent of Revascularization in Complex High Risk and Indicated Patients Undergoing Impella-Protected Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Report from the Roma-Verona Registry
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of extent of revascularization in complex high-risk indicated patients (CHIP) undergoing Impella-protected percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Background: Complete revascularization has been shown to be associated with improved outcomes. However, the impact of more complete revascularization during Impella-protected PCI in CHIP has not been reported.
Methods: A total of 86 CHIP undergoing elective PCI with Impella 2.5 or Impella CP between April 2007 and December 2016 from 2 high volume Italian centers were included. Baseline, procedural, and clinical outcomes data were collected retrospectively. Completeness of coronary revascularization was assessed using the British Cardiovascular Intervention Society myocardial jeopardy score (BCIS-JS) derived revascularization index (RI). The primary end-point was all-cause mortality. A multivariate regression model was used to identify independent predictors of mortality.
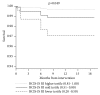
Results: All patients had multivessel disease and were considered unsuitable for surgery. At baseline, 44% had left main disease, 78% had LVEF ≤ 35%, and mean BCIS-JS score was 10±2. The mean BCIS-JS derived RI was 0.7±0.2 and procedural complications were uncommon. At 14-month follow-up, all-cause mortality was 10.5%. At follow-up, 67.4% of CHIP had LVEF ≥ 35% compared to 22.1% before Impella protected-PCI. Higher BCIS-JS RI was significantly associated with LVEF improvement (p=0.002). BCIS-JS RI of ≤ 0.8 (HR 0.11, 95% CI 0.01- 0.92, and p = 0.042) was an independent predictor of mortality.
Conclusions: These results support the practice of percutaneous Impella use for protected PCI in CHIP. A more complete revascularization was associated with significant LVEF improvement and survival.
Copyright © 2019 Francesco Burzotta et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Burzotta discloses to have been involved in advisory board meetings or having received speaker's fees from Medtronic, St Jude Medical, Abiomed, Biotronic. Dr. Trani discloses to have been involved in advisory board meetings or having received speaker's fees from St Jude Medical, Abiomed, Biotronic. Dr. Aurigemma has been involved in advisory board activities by Biotronic. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Dixon S. R., Henriques J. P., Mauri L., et al. A prospective feasibility trial investigating the use of the Impella 2.5 system in patients undergoing high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention (The PROTECT I Trial): initial U.S. experience. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions. 2009;2(2):91–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2008.11.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- O'Neill W. W., Kleiman N. S., Moses J., et al. A prospective, randomized clinical trial of hemodynamic support with impella 2.5 versus intra-aortic balloon pump in patients undergoing high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention: the PROTECT II study. Circulation. 2012;126(14):1717–1727. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.098194. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
