Skin and Soft Tissue Infection Treatment and Prevention Practices by Pediatric Infectious Diseases Providers
- PMID: 31773168
- PMCID: PMC7864142
- DOI: 10.1093/jpids/piz080
Skin and Soft Tissue Infection Treatment and Prevention Practices by Pediatric Infectious Diseases Providers
Abstract
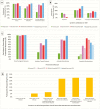
We surveyed 323 members of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society about their clinical practices for skin abscess management based on the 2011 Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines and contemporary evidence. Despite this guideline and recent randomized trials, variability exists among pediatric infectious diseases clinicians in current skin and soft tissue infection management practices.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; SSTI management; antibiotics; decolonization; skin and soft tissue infection.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Hersh AL, Chambers HF, Maselli JH, Gonzales R. National trends in ambulatory visits and antibiotic prescribing for skin and soft-tissue infections. Arch Intern Med 2008; 168:1585–91. - PubMed
-
- Moran GJ, Krishnadasan A, Gorwitz RJ, et al. ; EMERGEncy ID Net Study Group Methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections among patients in the emergency department. N Engl J Med 2006; 355:666–74. - PubMed
-
- Pallin DJ, Egan DJ, Pelletier AJ, et al. . Increased US emergency department visits for skin and soft tissue infections, and changes in antibiotic choices, during the emergence of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Emerg Med 2008; 51:291–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

