Sequential Ipilimumab After Chemoradiotherapy in Curative-Intent Treatment of Patients With Node-Positive Cervical Cancer
- PMID: 31774464
- PMCID: PMC6902184
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3857
Sequential Ipilimumab After Chemoradiotherapy in Curative-Intent Treatment of Patients With Node-Positive Cervical Cancer
Abstract
Importance: Despite standard chemoradiotherapy (CRT), most women with lymph node (LN)-positive cervical cancer experience disease recurrence. Immunotherapy is being investigated in the up-front treatment setting.
Objectives: To assess the safety of sequential immunotherapy after CRT and to investigate human papillomavirus (HPV) genotype and HLA allele status on survival and programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) expression before and after CRT and sequential immunotherapy.
Design, setting, and participants: This prospective phase 1 trial conducted in 29 Gynecology Oncology Cooperative Group member institutions enrolled participants from December 18, 2012, to August 31, 2016, with a 14.8-month median follow-up and translational end points. Thirty-four women with International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage IB2 to IVA cervical cancer with positive pelvic LNs, para-aortic LNs, or both were enrolled; 13 did not receive ipilimumab and were excluded from the analysis. Data were analyzed from January 21 to April 4, 2018.
Interventions: Treatment consisted of 6 weekly doses of cisplatin, 40 mg/m2, concurrent with radiotherapy. After completion of chemotherapy, sequential ipilimumab was given every 21 days for 4 doses. Two dosage levels of ipilimumab, 3 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg, were studied to identify the maximum tolerated dose.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was safety, and the secondary end points were overall survival and progression-free survival. Exploratory end points included HPV genotype, HLA allele status, and PD-1 expression measured in peripheral blood.
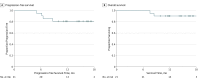
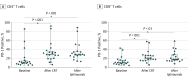
Results: The median age of the 32 participants included in the intent-to-treat analysis was 50 (range, 26-61) years, and 22 patients (69%) were white. Of the 21 patients who received ipilimumab, all had positive pelvic LN, and 6 (29%) had positive para-aortic LNs. All patients completed CRT, and of the 21 patients who received at least 2 cycles of ipilimumab, 18 (86%) completed 4 cycles of ipilimumab, and 3 (14%) completed 2 cycles. The maximum tolerated dose was 10 mg/kg. Two of the 21 patients (9.5%) who received ipilimumab had self-limiting grade 3 toxic effects (lipase increase; dermatitis). The 12-month overall survival was 90%, and progression-free survival was 81%. Human papillomavirus genotype and HLA subtype were not associated with progression-free survival or overall survival. T cells expressing PD-1 increased after CRT, and levels were sustained with ipilimumab.
Conclusions and relevance: This study's findings suggest that the use of immunotherapy after CRT for curative-intent treatment of patients with cervical cancer is tolerable and effective. The results indicated that PD-1 was upregulated after CRT and sustained with sequential ipilimumab therapy. These immune findings may help guide future therapies to harness the activated T-cell phenotype in patients with node-positive cervical cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Radiation for Cancers of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix: Incremental Steps, and Glimmers of the Future.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020 Nov 15;108(4):839-845. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.06.012. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020. PMID: 33069345 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cancer C. Cervical cancer. NIH Consens Statement. 1996;14(1):1-38. - PubMed
-
- Varia MA, Bundy BN, Deppe G, et al. Cervical carcinoma metastatic to para-aortic nodes: extended field radiation therapy with concomitant 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin chemotherapy: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;42(5):1015-1023. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3016(98)00267-3 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

