Superior Intellectual Outcomes After Proton Radiotherapy Compared With Photon Radiotherapy for Pediatric Medulloblastoma
- PMID: 31774710
- PMCID: PMC7007288
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.19.01706
Superior Intellectual Outcomes After Proton Radiotherapy Compared With Photon Radiotherapy for Pediatric Medulloblastoma
Abstract
Purpose: Proton radiotherapy (PRT) may lessen the neuropsychological risk traditionally associated with cranial radiotherapy for the treatment of pediatric brain tumors by reducing the dose to normal tissue compared with that of photon radiotherapy (XRT). We examined the change in intellectual scores over time in patients with pediatric medulloblastoma treated with craniospinal PRT versus XRT.
Methods: Intelligence test scores were obtained for a sample of pediatric patients treated between 2007 and 2018 on the same medulloblastoma protocols that differed only in radiotherapy modality (PRT v XRT). Growth curve analyses compared change in scores over time since diagnosis between groups.
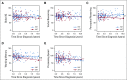
Results: Longitudinal intelligence data from 79 patients (37 PRT, 42 XRT) were examined. Groups were similar on most demographic/clinical variables, including sex (67.1% male), age at diagnosis (mean, 8.6 years), craniospinal irradiation dose (median, 23.4 Gy), length of follow-up (mean, 4.3 years), and parental education (mean, 14.3 years). Boost dose (P < .001) and boost margin (P = .001) differed between groups. Adjusting for covariates, the PRT group exhibited superior long-term outcomes in global intelligence quotient (IQ), perceptual reasoning, and working memory compared with the XRT group (all P < .05). The XRT group exhibited a significant decline in global IQ, working memory, and processing speed (all P < .05). The PRT group exhibited stable scores over time in all domains with the exception of processing speed (P = .003).
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first study to compare intellectual trajectories between pediatric patients treated for medulloblastoma with PRT versus those treated with XRT on comparable, contemporary protocols. PRT was associated with more favorable intellectual outcomes in most domains compared with XRT, although processing speed emerged as a vulnerable domain for both groups. This study provides the strongest evidence to date of an intellectual sparing advantage with PRT in the treatment of pediatric medulloblastoma.
Figures
Comment in
-
Intelligence outcomes after proton versus photon therapy.Lancet Oncol. 2020 Jan;21(1):e16. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30802-2. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Lancet Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31813777 No abstract available.
-
Association or Causality: Does Whole Brain Proton Radiotherapy Not Impact IQ?J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jul 1;38(19):2211-2212. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00019. Epub 2020 May 6. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32374642 No abstract available.
-
Reply to S.A. Milgrom et al.J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jul 1;38(19):2212-2213. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00344. Epub 2020 May 6. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32374644 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
[Is proton radiotherapy superior to photon radiotherapy in terms of intellectual outcome?].Strahlenther Onkol. 2020 Dec;196(12):1135-1138. doi: 10.1007/s00066-020-01692-y. Strahlenther Onkol. 2020. PMID: 32997188 Free PMC article. German. No abstract available.
References
-
- Mulhern RK, Merchant TE, Gajjar A, et al. Late neurocognitive sequelae in survivors of brain tumours in childhood. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5:399–408. - PubMed
-
- Moxon-Emre I, Bouffet E, Taylor MD, et al. Impact of craniospinal dose, boost volume, and neurologic complications on intellectual outcome in patients with medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:1760–1768. - PubMed
-
- Yock TI, Tarbell NJ. Technology insight: Proton beam radiotherapy for treatment in pediatric brain tumors. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2004;1:97–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

