Mifepristone and misoprostol versus misoprostol alone for uterine evacuation after early pregnancy failure: study protocol for a randomized double blinded placebo-controlled comparison (Triple M Trial)
- PMID: 31775677
- PMCID: PMC6880504
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-019-2497-y
Mifepristone and misoprostol versus misoprostol alone for uterine evacuation after early pregnancy failure: study protocol for a randomized double blinded placebo-controlled comparison (Triple M Trial)
Abstract
Background: Early pregnancy failure (EPF) is a common complication of pregnancy. If women do not abort spontaneously, they will undergo medical or surgical treatment in order to remove the products of conception from the uterus. Curettage, although highly effective, is associated with a risk of complications; medical treatment with misoprostol is a safe and less expensive alternative. Unfortunately, after 1 week of expectant management in case of EPF, medical treatment with misoprostol has a complete evacuation rate of approximately 50%. Misoprostol treatment results may be improved by pre-treatment with mifepristone; its effectiveness has already been proven for other indications of pregnancy termination. This study will test the hypothesis that, in EPF, the sequential combination of mifepristone with misoprostol is superior to the use of misoprostol alone in terms of complete evacuation (primary outcome), patient satisfaction, complications, side effects and costs (secondary outcomes).
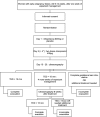
Methods: The trial will be performed multi-centred, prospectively, two-armed, randomised, double-blinded and placebo-controlled. Women with confirmed EPF by ultrasonography (6-14 weeks), managed expectantly for at least 1 week, can be included and randomised to pre-treatment with oral mifepristone (600 mg) or oral placebo (identical in appearance). Randomisation will take place after receiving written consent to participate. In both arms pre-treatment will be followed by oral misoprostol, which will start 36-48 h later consisting of two doses 400 μg (4 hrs apart), repeated after 24 h if no tissue is lost. Four hundred sixty-four women will be randomised in a 1:1 ratio, stratified by centre. Ultrasonography 2 weeks after treatment will determine short term treatment effect. When the gestational sac is expulsed, expectant management is advised until 6 weeks after treatment when the definitive primary endpoint, complete or incomplete evacuation, will be determined. A sonographic endometrial thickness < 15 mm using only the allocated therapy by randomisation is considered as successful treatment. Secondary outcome measures (patient satisfaction, complications, side effects and costs) will be registered using a case report form, patient diary and validated questionnaires (Short Form 36, EuroQol-VAS, Client Satisfaction Questionnaire, iMTA Productivity Cost Questionnaire).
Discussion: This trial will answer the question if, in case of EPF, after at least 1 week of expectant management, sequential treatment with mifepristone and misoprostol is more effective than misoprostol alone to achieve complete evacuation of the products of conception.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov (d.d. 02-07-2017): NCT03212352. Trialregister.nl (d.d. 03-07-2017): NTR6550. EudraCT number (d.d. 07-08-2017): 2017-002694-19. File number Commisie Mensgebonden Onderzoek (d.d. 07-08-2017): NL 62449.091.17.
Keywords: Early pregnancy failure; Mifepristone; Miscarriage; Misoprostol; Missed abortion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Open data van de Nederlandse Zorgautoriteit (2014-2016) [http://www.opendisdata.nl/].
-
- Hooker AB, Lemmers M, Thurkow AL, Heymans MW, Opmeer BC, Brolmann HA, Mol BW, Huirne JA. Systematic review and meta-analysis of intrauterine adhesions after miscarriage: prevalence, risk factors and long-term reproductive outcome. Hum Reprod Update. 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical