Acclimation to a thermoneutral environment abolishes age-associated alterations in heart rate and heart rate variability in conscious, unrestrained mice
- PMID: 31776883
- PMCID: PMC7031176
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-019-00126-7
Acclimation to a thermoneutral environment abolishes age-associated alterations in heart rate and heart rate variability in conscious, unrestrained mice
Abstract
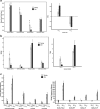
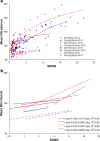
Mice are among the most widely used translational models of cardiovascular aging and offer a method to quickly assess lifespan changes in a controlled environment. The standard laboratory temperature (20-22 °C), however, imposes a cold stress on mice that causes an increase in sympathetic nervous system-mediated activation of brown adipose tissue (BAT) to maintain a core body temperature of 36-37 °C. Thus, while physiologic data obtained recapitulate human physiology to a certain degree, interpretations of previous research in mice may have been contaminated by a cold stress, due to housing mice below their thermoneutral zone (30 °C). The purpose of this investigation was to examine how chronic sympathetic stimulation evoked by acclimation to 20 °C might obscure interpretation of changes in autonomic modulation of heart rate (HR) and heart rate variability (HRV) that accompany advancing age. HR and HRV before and after administration of a dual-autonomic blockade were measured via in-vivo ECG in young (3 months) and aged (30 months) male C57BL/6 telemetry-implanted mice following temperature acclimation for 3 days at 30 °C or 20 °C. Mean basal and intrinsic HR of both young and aged mice became markedly reduced at 30 °C compared to 20 °C. In both age groups, HRV parameters in time, frequency, and non-linear domains displayed increased variability at 30 °C compared to 20 °C under basal conditions. Importantly, age-associated declines in HRV observed at 20 °C were ameliorated when mice were studied at their thermoneutral ambient temperature of 30 °C. Thus, an accurate understanding of autonomic modulation of cardiovascular functions in mice of advanced age requires that they are housed in a metabolically neutral environment.
Keywords: Aging; Cardiac autonomic modulation; Heart rate; Heart rate variability; Thermoneutrality.
Figures



References
-
- Antelmi I, De Paula RS, Shinzato AR, Peres CA, Mansur AJ, Grupi CJ. Influence of age, gender, body mass index, and functional capacity on heart rate variability in a cohort of subjects without heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 2004;93(3):381–385. - PubMed
-
- Bigger JT, Jr, Fleiss JL, Steinman RC, Rolnitzky LM, Kleiger RE, Rottman JN. Correlations among time and frequency domain measures of heart period variability two weeks after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 1992;69(9):891–898. - PubMed
-
- Bigger JT, Jr, Fleiss JL, Steinman RC, Rolnitzky LM, Kleiger RE, Rottman JN. Frequency domain measures of heart period variability and mortality after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1992;85(1):164–171. - PubMed
-
- Bigger JT, Jr, Fleiss JL, Rolnitzky LM, Steinman RC. Frequency domain measures of heart period variability to assess risk late after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;21(3):729–736. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

