The effects of intravitreal H2 S application on apoptosis in the retina and cornea in experimental glaucoma model
- PMID: 31777145
- PMCID: PMC7042745
- DOI: 10.1111/iep.12334
The effects of intravitreal H2 S application on apoptosis in the retina and cornea in experimental glaucoma model
Abstract
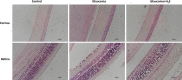
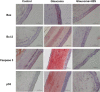
One of the most important causes of visual loss (blindness) is glaucoma, which occurs due to the degeneration of the ganglion cells in retina. It has been shown that hydrogen sulphide (H2 S) acts an antioxidant, neuroprotective and neuromodulator and provides protection against oxidative stress and apoptosis. This study aims to examine through which apoptotic pathway H2 S acts in experimental glaucoma model. Twenty-two male wistar albino rats were used in this study. Group 1 (n = 6, control group): Intravitreal saline was given in the third week without inducing ocular hypertension (OHT) with laser photocoagulation. Group 2 (n = 8): After the induction of OHT with laser photocoagulation, intravitreal saline was given in the third week. Group 3 (n = 8): After the induction of OHT with laser photocoagulation, intravitreal H2 S's donor sodium hydrosulphide (NaSH) 100 nmol/L was given in the third week. At the end of the 6th week, the eyes of the rats were sacrified under anaesthesia and extracted and then routine tissue follow-up was undertaken. Besides haematoxylin & eosin (H&E) staining, Bax, Bcl-2, p53 and caspase-3 activation were examined immunohistochemically in the retina and the cornea. This showed that ocular hypertension caused apoptosis through the intrinsic pathway, due to Bax and caspase-3 activation, in both retina and cornea, and that this led to DNA damage due to p53 activation. Also, we found that H2 S exposure in glaucoma distinctly suppressed Bax, caspase-3 and p53 activations in retina but that it has a limited effect on the cornea. According to these results, glaucoma caused apoptosis in the retina through intrinsic pathway, and the damage to the retina could be compensated partially by H2 S but would have limited on the cornea.
Keywords: apoptosis; cornea; glaucoma; hydrogen sulphide; rat; retina.
© 2019 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2019 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hydrogen sulfide supplement attenuates the apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells in experimental glaucoma.Exp Eye Res. 2018 Mar;168:33-48. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2018.01.004. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Exp Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29326065
-
Protective effect of molecular hydrogen against oxidative stress caused by peroxynitrite derived from nitric oxide in rat retina.Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015 Aug;43(6):568-77. doi: 10.1111/ceo.12525. Epub 2015 May 13. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25801048
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Magnesium Acetyltaurate Against NMDA-Induced Excitotoxicity in Rat Retina.Neurotox Res. 2017 Jan;31(1):31-45. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9658-9. Epub 2016 Aug 27. Neurotox Res. 2017. PMID: 27568334
-
The molecular basis of retinal ganglion cell death in glaucoma.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012 Mar;31(2):152-81. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2011.11.002. Epub 2011 Dec 4. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012. PMID: 22155051 Review.
-
Recent advances in the role of endogenous hydrogen sulphide in cancer cells.Cell Prolif. 2023 Sep;56(9):e13449. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13449. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 36929586 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of trabecular meshwork-specific promoters in vitro and in vivo using scAAV2 vectors expressing C3 transferase.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Aug 18;16(8):1196-1209. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.08.03. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37602341 Free PMC article.
-
Altered transsulfuration pathway enzymes and redox homeostasis in inherited retinal degenerative diseases.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Feb;215:108902. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108902. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 34954206 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis in glaucoma: A new direction for the treatment of glaucoma (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 May;29(5):82. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13207. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38516770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Evaluation of Puerarin Loaded-Albumin Nanoparticles Thermoresponsive in situ Gel for Ophthalmic Delivery.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Sep 27;16:3315-3326. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S374061. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 36193285 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the Neuroprotective Effect of Riluzole on Matrix Metalloproteinases in an Experimental Model of Glaucoma.J Curr Ophthalmol. 2025 Jan 18;36(2):136-144. doi: 10.4103/joco.joco_290_23. eCollection 2024 Apr-Jun. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40012807 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

