Biomechanical Factors in Psoriatic Disease: Defective Repair Exertion as a Potential Cause. Hypothesis Presentation and Literature Review
- PMID: 31777825
- PMCID: PMC6858026
- DOI: 10.1002/acr2.11056
Biomechanical Factors in Psoriatic Disease: Defective Repair Exertion as a Potential Cause. Hypothesis Presentation and Literature Review
Abstract
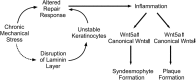
Joining main clinical manifestations of psoriatic skin disorder are inflammatory arthritis and nail lesions. Repetitive microdamage has been postulated as a main triggering factor in lesions of psoriatic arthritis. This concept of psoriatic disease might also be admissible for triggering nail lesions because the nail is a frequently traumatized structure. Here, we aimed to describe the conjectural injury mechanisms of nail complex with regard to acting biomechanical factors. Tissue repair response to physical microdamage may be altered in psoriatic disease. It is plausible to consider that a defective repair process in the dysregulated prepsoriatic tissue may lead to innate immune activation and further development of autoinflammatory lesions, although excessive inflammation is known to impair wound healing. Recently published data have revealed the importance of mechanosensitive Wingless-type (Wnt) signaling in the pathophysiology of psoriasis and ankylosing spondylitis. The Wnt signaling system is involved in morphogenesis, repair, and regeneration as a biologic process main regulator. Wnt5a seems to be a dominating mediator in both psoriatic plaques and during the spondylitis process that might also be a linking molecule of psoriatic response to mechanical stress. Future studies should focus on complex responsive interactions of tissue repair regulators regarded in psoriatic disease.
© 2019, The Authors. ACR Open Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Parisi R, Symmons DP, Griffiths CE, Ashcroft DM. Identification and Management of Psoriasis and Associated ComorbidiTy (IMPACT) project team. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J Invest Dermatol 2013;133:377–85. - PubMed
-
- Köbner H. Zur aetiologie der psoriasis. Vjschr Dermatol 1876;3:559.
-
- Boyd AS, Neldner KH. The isomorphic response of Koebner. Int J Dermatol 1990;29:401–10. - PubMed
-
- Thappa DM. The isomorphic phenomenon of Koebner. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2004;70:187–9. - PubMed
-
- Farber EM, Roth RJ, Aschheim E, Eddy DD, Epinette WW. Role of trauma in isomorphic response in psoriasis. Arch Dermatol 1965;91:246–251. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials