Supramolecular Solvent-Based Liquid Phase Microextraction Combined with Ion-Pairing Reversed-Phase HPLC for the Determination of Quats in Vegetable Samples
- PMID: 31779095
- PMCID: PMC6958504
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics7040060
Supramolecular Solvent-Based Liquid Phase Microextraction Combined with Ion-Pairing Reversed-Phase HPLC for the Determination of Quats in Vegetable Samples
Abstract
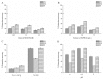
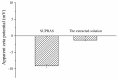
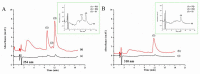
In this study, we used anion supramolecular solvent (SUPRAS) prepared from a mixture of an anionic surfactant, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and a cationic surfactant, tetrabutylammonium bromide (TBABr), as the extraction solvent in liquid phase microextraction (LPME) of paraquat (PQ) and diquat (DQ). The enriched PQ and DQ in the SUPRAS phase were simultaneously analyzed by ion-pairing reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. PQ and DQ were successfully extracted by LPME via electrostatic interaction between the positive charge of the quats and the negative charge of SUPRAS. PQ, DQ, and ethyl viologen (the internal standard) were separated within 15 min on a C18 column, with the mobile phase containing 1-dodecanesulfonic acid and triethylamine, via UV detection. The optimized conditions for the extraction of 10 mL aqueous solution are 50 μL of SUPRAS prepared from a mixture of SDS and TBABr at a mole ratio of 1:0.5, vortexed for 10 s at 1800 rpm, and centrifugation for 1 min at 3500 rpm. The obtained enrichment factors were 22 and 26 with limits of detection of 1.5 and 2.8 µg L-1 for DQ and PQ, respectively. The precision was good with relative standard deviations less than 3.86%. The proposed method was successfully applied for the determination of PQ and DQ in vegetable samples and recoveries were found in the range of 75.0% to 106.7%.
Keywords: ion-pairing reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography (IP-RPHPLC); liquid phase microextraction (LPME); quaternary ammonium compounds (quats); supramolecular solvent (SUPRAS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Carneiro M.C., Puignou L., Galceran M.T. Comparison of silica and porous graphitic carbon as solid-phase extraction materials for the analysis of cationic herbicides in water by liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2000;408:263–269. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(99)00830-2. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

