Development of Targeted Alpha Particle Therapy for Solid Tumors
- PMID: 31779154
- PMCID: PMC6930656
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24234314
Development of Targeted Alpha Particle Therapy for Solid Tumors
Abstract
Targeted alpha-particle therapy (TAT) aims to selectively deliver radionuclides emitting α-particles (cytotoxic payload) to tumors by chelation to monoclonal antibodies, peptides or small molecules that recognize tumor-associated antigens or cell-surface receptors. Because of the high linear energy transfer (LET) and short range of alpha (α) particles in tissue, cancer cells can be significantly damaged while causing minimal toxicity to surrounding healthy cells. Recent clinical studies have demonstrated the remarkable efficacy of TAT in the treatment of metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer. In this comprehensive review, we discuss the current consensus regarding the properties of the α-particle-emitting radionuclides that are potentially relevant for use in the clinic; the TAT-mediated mechanisms responsible for cell death; the different classes of targeting moieties and radiometal chelators available for TAT development; current approaches to calculating radiation dosimetry for TATs; and lead optimization via medicinal chemistry to improve the TAT radiopharmaceutical properties. We have also summarized the use of TATs in pre-clinical and clinical studies to date.
Keywords: chelation; clinical studies; mechanism of cell death; medicinal chemistry; radiation dosimetry; solid tumors; targeted alpha-particle therapy; targeting moieties.
Conflict of interest statement
Doctors Morse, Wadas, McLaughlin and Tafreshi are co-inventors on a patent-pending application for a novel uveal melanoma TAT. The patent pending has been licensed to Modulation Therapeutics Inc. and Dr. McLaughlin is a co-founder of that company. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

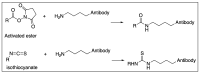
References
-
- Sgouros G., Roeske J.C., McDevitt M.R., Palm S., Allen B.J., Fisher D.R., Brill A.B., Song H., Howell R.W., Akabani G., et al. MIRD Pamphlet No. 22 (abridged): Radiobiology and dosimetry of alpha-particle emitters for targeted radionuclide therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2010;51:311–328. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.108.058651. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dizdarevic S., Jessop M., Begley P., Main S., Robinson A. (223)Ra-Dichloride in castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer: Improving outcomes and identifying predictors of survival in clinical practice. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2018;45:2264–2273. doi: 10.1007/s00259-018-4083-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kratochwil C., Bruchertseifer F., Rathke H., Hohenfellner M., Giesel F.L., Haberkorn U., Morgenstern A. Targeted alpha-Therapy of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer with (225)Ac-PSMA-617: Swimmer-Plot Analysis Suggests Efficacy Regarding Duration of Tumor Control. J. Nucl. Med. 2018;59:795–802. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.117.203539. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

