Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus with a possible paraneoplastic association with melanoma
- PMID: 31780613
- PMCID: PMC6887353
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2019-230558
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus with a possible paraneoplastic association with melanoma
Abstract
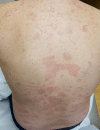
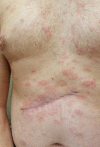
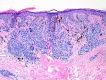
A 52-year-old man was referred to our dermatology clinic for a diagnosis of melanoma. At the time, his melanoma was excised he developed an annular, polycyclic, scaling eruption consistent with subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE). Skin biopsy and laboratory evaluation confirmed this diagnosis. The patient had been using pantoprazole for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease for the last 3 years. The patient's melanoma was treated surgically, and his SCLE was treated with topical steroids and hydroxychloroquine. His SCLE cleared rapidly, his steroids and hydroxychloroquine were stopped and he remains free of SCLE off of treatment. The parallel course of the patient's SCLE and melanoma prompted consideration of SCLE as paraneoplastic to melanoma in this case. The clinical picture was complicated by the patient's use of a proton pump inhibitor, which are common causes of drug-induced SCLE. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of possible paraneoplastic SCLE associated with melanoma.
Keywords: dermatology; drugs and medicines; oncology; rheumatology.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2019. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Mortazie M, Ramirez J, LaFond A. A case of paraneoplastic subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016;AB78.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
