Structural and Functional Determinants of Rodent and Human Surfactant Protein A: A Synthesis of Binding and Computational Data
- PMID: 31781112
- PMCID: PMC6856657
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02613
Structural and Functional Determinants of Rodent and Human Surfactant Protein A: A Synthesis of Binding and Computational Data
Abstract
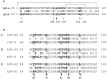
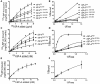
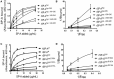
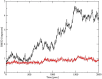
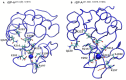
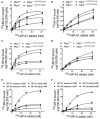
Surfactant protein A (SP-A) provides surfactant stability, first line host defense, and lung homeostasis by binding surfactant phospholipids, pathogens, alveolar macrophages (AMs), and epithelial cells. Non-primates express one SP-A protein whereas humans express two: SP-A1 and SP-A2 with core intra- and inter-species differences in the collagen-like domain. Here, we used macrophages and solid phase binding assays to discern structural correlates of rat (r) and human (h) SP-A function. Binding assays using recombinant rSP-A expressed in insect cells showed that lack of proline hydroxylation, truncations of amino-terminal oligomerization domains, and site-directed serine (S) or alanine (A) mutagenesis of cysteine 6 (C6S), glutamate 195 (E195A), and glutamate 171 (E171A) in the carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) all impaired SP-A binding. Replacement of arginine 197 with alanine found in hSP-A (R197A), however, restored the binding of hydroxyproline-deficient rSP-A to the SP-A receptor SP-R210 similar to native rat and human SP-A. In silico calculation of Ca++ coordination bond length and solvent accessibility surface area revealed that the "humanized" R197A substitution alters topology and solvent accessibility of the Ca++ coordination residues of the CRD domain. Binding assays in mouse AMs that were exposed to either endogenous SP-A or hSP-A1 (6A2) and hSP-A2 (1A0) isoforms in vivo revealed that mouse SP-A is a functional hybrid of hSP-A1 and hSP-A2 in regulating SP-A receptor occupancy and binding affinity. Binding assays using neonatal and adult human AMs indicates that the interaction of SP-A1 and SP-A2 with AMs is developmentally regulated. Furthermore, our data indicate that the auxiliary ion coordination loop encompassing the conserved E171 residue may comprise a conserved site of interaction with macrophages, and SP-R210 specifically, that merits further investigation to discern conserved and divergent SP-A functions between species. In summary, our findings support the notion that complex structural adaptation of SP-A regulate conserved and species specific AM functions in vertebrates.
Keywords: alveolar macrophages; binding; lung; receptor; surfactant protein A.
Copyright © 2019 Nalian, Umstead, Yang, Silveyra, Thomas, Floros, McCormack and Chroneos.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human Surfactant Protein SP-A1 and SP-A2 Variants Differentially Affect the Alveolar Microenvironment, Surfactant Structure, Regulation and Function of the Alveolar Macrophage, and Animal and Human Survival Under Various Conditions.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 17;12:681639. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.681639. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the degree of oligomerization in the structure and function of human surfactant protein A.J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 4;280(9):7659-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410266200. Epub 2004 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15615713
-
Sex-Specific Regulation of Gene Expression Networks by Surfactant Protein A (SP-A) Variants in Alveolar Macrophages in Response to Klebsiella pneumoniae.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 24;11:1290. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01290. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32670284 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary surfactant protein A up-regulates activity of the mannose receptor, a pattern recognition receptor expressed on human macrophages.J Immunol. 2002 Oct 1;169(7):3565-73. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.7.3565. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12244146
-
Genetic complexity of the human innate host defense molecules, surfactant protein A1 (SP-A1) and SP-A2--impact on function.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2009;19(2):125-37. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v19.i2.30. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2009. PMID: 19392648 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human Surfactant Protein SP-A1 and SP-A2 Variants Differentially Affect the Alveolar Microenvironment, Surfactant Structure, Regulation and Function of the Alveolar Macrophage, and Animal and Human Survival Under Various Conditions.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 17;12:681639. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.681639. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in the alveolar macrophage toponome in humanized SP-A1 and SP-A2 transgenic mice.JCI Insight. 2020 Dec 17;5(24):e141410. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.141410. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 33141765 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Redox Status in the Frame of Lifestyle Approaches and the Genetics of the Lung Innate Immune Molecules, SP-A1 and SP-A2, on Differential Outcomes of COVID-19 Infection.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Aug 25;9(9):784. doi: 10.3390/antiox9090784. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32854247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory roles of SP-A and exosomes in pneumonia-induced acute lung and kidney injuries.Front Immunol. 2023 May 15;14:1188023. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1188023. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37256132 Free PMC article.
-
SP-R210 isoforms of Myosin18A modulate endosomal sorting and recognition of influenza A virus infection in macrophages.Microbes Infect. 2024 Mar-Apr;26(3):105280. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2023.105280. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 38135024 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

