Genetic and Functional Variants Analysis of the GATA6 Gene Promoter in Acute Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 31781165
- PMCID: PMC6851265
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01100
Genetic and Functional Variants Analysis of the GATA6 Gene Promoter in Acute Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
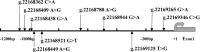
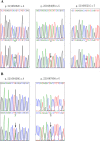
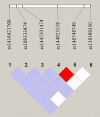
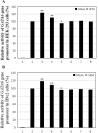
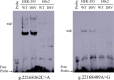
Background: Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) which is a specific type of coronary artery disease (CAD), is caused by the combination of genetic factors and acquired environment. Although some common genetic variations have been recorded to contribute to the development of CAD and AMI, more genetic factors and potential molecular mechanisms remain largely unknown. The GATA6 gene is expressed in the heart during embryogenesis and is also detected in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), different human primary endothelial cells (ECs), and vascular ECs in mice. To date, no studies have directly linked GATA6 gene with regulation of the CAD. Methods: In this study, we used a case-control study to investigate and analyze the genetic variations and functional variations of the GATA6 gene promoter region in AMI patients and controls. A variety of statistical analysis methods were utilized to analyze the association of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with AMI. Functional analysis of DNA sequence variants (DSVs) was performed using a dual luciferase reporter assay. In vitro, electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) was selected to examine DNA-protein interactions. Results: A total of 705 subjects were enrolled in the study. Ten DSVs were found in AMI patients (n = 352) and controls (n = 353), including seven SNPs. One novel heterozygous DSV, (g.22168409 A > G), and two SNPs, [g.22168362 C > A(rs1416421760) and g.22168521 G > T(rs1445501474)], were reported in three AMI patients, which were not found in controls. The relevant statistical analysis, including allele and genotype frequencies between AMI patients and controls, five genetic models, linkage disequilibrium (LD) and haplotype analysis, and SNP-SNP interactions, suggested no statistical significance (P > 0.05). The transcriptional activity of GATA6 gene promoter was significantly increased by the DSV (g.22168409 A > G) and SNP [g.22168362 C > A(rs1416421760)]. The EMSA revealed that the DSV (g.22168409 A > G) and SNP [g.22168362 C > A(rs1416421760)] evidently influenced the binding of transcription factors. Conclusion: In conclusion, the DSV (g.22168409 A > G) and SNP [g.22168362 C > A(rs1416421760)] may increase GATA6 levels in both HEK-293 and H9c2 cell lines by affecting the binding of transcription factors. Whether the two variants identified in the GATA6 gene promoter can promote the development and progression of human AMI by altering GATA6 levels still requires further studies to verify.
Keywords: GATA binding protein 6; acute myocardial infarction; gene expression regulation; genetic variants; promoter; single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Copyright © 2019 Sun, Pang, Cui and Yan.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional genetic variants in the SIRT5 gene promoter in acute myocardial infarction.Gene. 2018 Oct 30;675:233-239. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.07.010. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29981421
-
Molecular genetic study on GATA5 gene promoter in acute myocardial infarction.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 8;16(3):e0248203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248203. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33684162 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Genetic variants of VEGFR-1 gene promoter in acute myocardial infarction.Hum Genomics. 2019 Nov 19;13(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s40246-019-0243-1. Hum Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31744542 Free PMC article.
-
Functional variants in the LC3B gene promoter in acute myocardial infarction.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Sep;119(9):7339-7349. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27035. Epub 2018 May 15. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29761913
-
Genetic risk factors in myocardial infarction at young age.Minerva Cardioangiol. 2004 Aug;52(4):287-312. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2004. PMID: 15284679 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Association Studies for Milk Somatic Cell Score in Romanian Dairy Cattle.Genes (Basel). 2021 Sep 24;12(10):1495. doi: 10.3390/genes12101495. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680890 Free PMC article.
-
From multi-omics approaches to personalized medicine in myocardial infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Oct 30;10:1250340. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1250340. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37965091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GATA6-AS1 Regulates GATA6 Expression to Modulate Human Endoderm Differentiation.Stem Cell Reports. 2020 Sep 8;15(3):694-705. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.07.014. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Stem Cell Reports. 2020. PMID: 32795420 Free PMC article.
-
A novel causative functional mutation in GATA6 gene is responsible for familial dilated cardiomyopathy as supported by in silico functional analysis.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 12;12(1):13752. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13993-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35962153 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and prealbumin with coronary vessels stenosis determined by coronary angiography and heart failure in patients with myocardial infarction.J Med Biochem. 2023 Jan 20;42(1):9-15. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-37847. J Med Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36819129 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

