Translated Long Non-Coding Ribonucleic Acid ZFAS1 Promotes Cancer Cell Migration by Elevating Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 31781169
- PMCID: PMC6861293
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01111
Translated Long Non-Coding Ribonucleic Acid ZFAS1 Promotes Cancer Cell Migration by Elevating Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
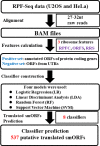
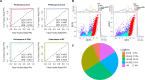
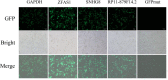
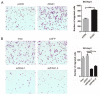
Micropeptides (≤100 amino acids) are essential regulators of physiological and pathological processes, which can be encoded by small open reading frames (smORFs) derived from long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). Recently, lncRNA-encoded micropeptides have been shown to have essential roles in tumorigenesis. Since translated smORF identification remains technically challenging, little is known of their pathological functions in cancer. Therefore, we created classifiers to identify translated smORFs derived from lncRNAs based on ribosome-protected fragment sequencing and machine learning methods. In total, 537 putative translated smORFs were identified and the coding potential of five smORFs was experimentally validated via green fluorescent protein-tagged protein generation and mass spectrometry. After analyzing 11 lncRNA expression profiles of seven cancer types, we identified one validated translated lncRNA, ZFAS1, which was significantly up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Functional studies revealed that ZFAS1 can promote cancer cell migration by elevating intracellular reactive oxygen species production by inhibiting nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase expression, indicating that translated ZFAS1 may be an essential oncogene in the progression of HCC. In this study, we systematically identified translated smORFs derived from lncRNAs and explored their potential pathological functions in cancer to improve our comprehensive understanding of the building blocks of living systems.
Keywords: ZFAS1; hepatocellular carcinoma; reactive oxygen species; ribosome-protected fragment sequencing; translated small open reading frames.
Copyright © 2019 Guo, Meng, Zhai, Xie, Zhao, Li, Zhou, Li, Liu, Yang and Wu.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Viral Infection Identifies Micropeptides Differentially Regulated in smORF-Containing lncRNAs.Genes (Basel). 2017 Aug 21;8(8):206. doi: 10.3390/genes8080206. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28825667 Free PMC article.
-
Pervasive translation of small open reading frames in plant long non-coding RNAs.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 24;13:975938. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.975938. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36352887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A vast pool of lineage-specific microproteins encoded by long non-coding RNAs in plants.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Oct 11;49(18):10328-10346. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab816. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34570232 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated workflow for discovery of microprotein-coding small open reading frames.STAR Protoc. 2023 Dec 15;4(4):102649. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2023.102649. Epub 2023 Oct 23. STAR Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37874679 Free PMC article.
-
ZFAS1: a novel tumor-related long non-coding RNA.Cancer Cell Int. 2018 Sep 3;18:125. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0623-y. eCollection 2018. Cancer Cell Int. 2018. PMID: 30186041 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Long Noncoding RNA ZFAS1 Potentiates the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via the microRNA-624/MDK/ERK/JNK/P38 Signaling Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 19;13:4431-4444. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S246278. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32547074 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Dark Matter of Human Proteome: The Emerging Role of Non-Canonical Open Reading Frame (ncORF) in Cancer Diagnosis, Biology, and Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 26;16(15):2660. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152660. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Subpathway and Target Gene Cluster-Based Approach Uncovers lncRNAs Associated with Human Primordial Follicle Activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 23;24(13):10525. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310525. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445702 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and implications of de novo genes in humans.Nat Ecol Evol. 2023 Jun;7(6):804-815. doi: 10.1038/s41559-023-02014-y. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Nat Ecol Evol. 2023. PMID: 36928843 Review.
-
Chlamydia trachomatis Plasmid Protein pORF5 Up-Regulates ZFAS1 to Promote Host Cell Survival via MAPK/p38 Pathway.Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 17;11:593295. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.593295. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33391210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breiman L. (2001). Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 45, 5–32. 10.1023/A:1010933404324 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

