Hypoxic Preconditioning Enhances Survival and Proangiogenic Capacity of Human First Trimester Chorionic Villus-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Fetal Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 31781252
- PMCID: PMC6874947
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9695239
Hypoxic Preconditioning Enhances Survival and Proangiogenic Capacity of Human First Trimester Chorionic Villus-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Fetal Tissue Engineering
Abstract
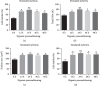
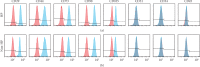
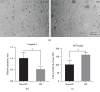
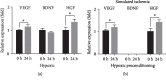
Prenatal stem cell-based regenerative therapies have progressed substantially and have been demonstrated as effective treatment options for fetal diseases that were previously deemed untreatable. Due to immunoregulatory properties, self-renewal capacity, and multilineage potential, autologous human placental chorionic villus-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (CV-MSCs) are an attractive cell source for fetal regenerative therapies. However, as a general issue for MSC transplantation, the poor survival and engraftment is a major challenge of the application of MSCs. Particularly for the fetal transplantation of CV-MSCs in the naturally hypoxic fetal environment, improving the survival and engraftment of CV-MSCs is critically important. Hypoxic preconditioning (HP) is an effective priming approach to protect stem cells from ischemic damage. In this study, we developed an optimal HP protocol to enhance the survival and proangiogenic capacity of CV-MSCs for improving clinical outcomes in fetal applications. Total cell number, DNA quantification, nuclear area test, and cell viability test showed HP significantly protected CV-MSCs from ischemic damage. Flow cytometry analysis confirmed HP did not alter the immunophenotype of CV-MSCs. Caspase-3, MTS, and Western blot analysis showed HP significantly reduced the apoptosis of CV-MSCs under ischemic stimulus via the activation of the AKT signaling pathway that was related to cell survival. ELISA results showed HP significantly enhanced the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) by CV-MSCs under an ischemic stimulus. We also found that the environmental nutrition level was critical for the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). The angiogenesis assay results showed HP-primed CV-MSCs could significantly enhance endothelial cell (EC) proliferation, migration, and tube formation. Consequently, HP is a promising strategy to increase the tolerance of CV-MSCs to ischemia and improve their therapeutic efficacy in fetal clinical applications.
Copyright © 2019 Dake Hao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Self-assembled GFFYK peptide hydrogel enhances the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse hindlimb ischemia model.Acta Biomater. 2019 Feb;85:94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.12.015. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30550934
-
Hypoxic Preconditioning Increases Survival and Pro-Angiogenic Capacity of Human Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stromal Cells In Vitro.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 18;10(9):e0138477. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138477. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26380983 Free PMC article.
-
A nitric oxide-releasing hydrogel for enhancing the therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for hindlimb ischemia.Acta Biomater. 2020 Sep 1;113:289-304. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.07.011. Epub 2020 Jul 11. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32663662
-
Priming strategies for controlling stem cell fate: Applications and challenges in dental tissue regeneration.World J Stem Cells. 2021 Nov 26;13(11):1625-1646. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i11.1625. World J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 34909115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxic culture conditions as a solution for mesenchymal stem cell based regenerative therapy.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Aug 27;2013:632972. doi: 10.1155/2013/632972. eCollection 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 24068884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Photobiomodulation in 3D tissue engineering.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Sep;27(9):090901. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.9.090901. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 36104833 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of preconditioning hypoxia in schwann-like-cells-derived adipose mesenchymal stem cells and rat sciatic nerve-derived stem cells: experimental research.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 May 6;85(7):3439-3445. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000777. eCollection 2023 Jul. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37427197 Free PMC article.
-
Ex Vivo Preconditioning as a Useful Tool for Modification of the Extracellular Matrix of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 30;26(13):6301. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136301. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developing an Injectable Nanofibrous Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel With an Integrin αvβ3 Ligand to Improve Endothelial Cell Survival, Engraftment and Vascularization.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 29;8:890. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00890. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32850742 Free PMC article.
-
State of the field: cellular and exosomal therapeutic approaches in vascular regeneration.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Apr 1;322(4):H647-H680. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00674.2021. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35179976 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fridenshteĭn A., Petrakova K. V., Kuralesova A. I., Frolova G. I. Precursor cells for osteogenic and hemopoietic tissues. Analysis of heterotopic transplants of bone marrow. Tsitologiia. 1968;10(5):557–567. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

