Jieduquyuziyin Prescription-Treated Rat Serum Suppresses Activation of Peritoneal Macrophages in MRL/Lpr Lupus Mice by Inhibiting IRAK1 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 31781262
- PMCID: PMC6875022
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/2357217
Jieduquyuziyin Prescription-Treated Rat Serum Suppresses Activation of Peritoneal Macrophages in MRL/Lpr Lupus Mice by Inhibiting IRAK1 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
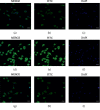
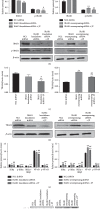
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease, and Jieduquyuziyin prescription (JP) is a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formula that has been testified to be effective for SLE treatment as an approved hospital prescription for many years in China. However, its mechanism of action in the treatment of this disease is largely unknown. The purpose of this study was to determine whether JP-treated rat serum can inhibit the activation of peritoneal macrophages in MRL/lpr mice by downregulating the IRAK1 signaling pathway, thereby achieving the effect of improving SLE. The JP-treated rat serum was prepared, and the peritoneal macrophages of MRL/lpr lupus mice were isolated in vitro, and the effect of JP on cell viability was detected by the CCK8 method. After LPS induction and shRNA lentiviral transfection, the effect of JP on the expression of IRAK1 in cells was detected by immunofluorescence staining. The content of TNF-α and IL-6 in the cell supernatant was determined by ELISA. The expression of IRAK1, NF-κB, TNF-α, and IL-6 mRNA was detected by RT-PCR, and the expression levels of IRAK1, p-IRAK1, TRAF6, IKBα, p-IKBα, IKK + IKK, NF-κB, and p-NF-κB proteins was detected by western blot method. We investigated the role of JP in peritoneal macrophages of the MRL/lpr mouse and identified the possible mechanisms of action. The results showed that JP could reduce the phosphorylation of IRAK1 and its downstream proteins induced by LPS and inhibit the expression of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6. In addition, after the transfection of cells with shRNA lentiviral, the results of JP tended to be consistent. In conclusion, JP may inhibit the activation of peritoneal macrophages in MRL/lpr mice by downregulating the IRAK1-NF-κB signaling pathway, and IRAK1 may be a potential target for JP treatment of SLE.
Copyright © 2019 Lina Ji et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Jieduquyuziyin Prescription Suppresses Inflammatory Activity of MRL/lpr Mice and Their Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages via Inhibiting Expression of IRAK1-NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 14;11:1049. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01049. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32760274 Free PMC article.
-
Paeoniflorin inhibits activation of the IRAK1-NF-κB signaling pathway in peritoneal macrophages from lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice.Microb Pathog. 2018 Nov;124:223-229. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.08.051. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30149133
-
Jieduquyuziyin Prescription alleviates hepatic gluconeogenesis via PI3K/Akt/PGC-1α pathway in glucocorticoid-induced MRL/lpr mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Feb 10;284:114815. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114815. Epub 2021 Nov 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34763039
-
Jieduquyuziyin prescription suppresses IL-17 production and Th17 activity in MRL/lpr mice by inhibiting expression of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-4.J Nat Med. 2015 Jul;69(3):349-57. doi: 10.1007/s11418-015-0900-1. Epub 2015 Mar 28. J Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 25821132
-
Jieduquyuziyin prescription enhances CD11a and CD70 DNA methylation of CD4+ T cells via miR-29b-sp1/DNMT1 pathway in MRL/lpr mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Dec 5;317:116776. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116776. Epub 2023 Jun 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37343653
Cited by
-
Paeoniflorin Inhibits LPS-Induced Activation of Splenic CD4+ T Lymphocytes and Relieves Pathological Symptoms in MRL/lpr Mice by Suppressing IRAK1 Signaling.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Nov 23;2022:5161890. doi: 10.1155/2022/5161890. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36467552 Free PMC article.
-
Jieduquyuziyin prescription attenuates the side effect of prednisone through regulating gut microbiota when in the combination with prednisone treat MRL/lpr mice.J Tradit Complement Med. 2024 May 24;15(2):119-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2024.05.005. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Tradit Complement Med. 2024. PMID: 40060153 Free PMC article.
-
Lupus Recipe inhibits cGVHD-induced lupus nephritis in mice and promote renal LC3-associated autophagy.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Mar;11(3):e815. doi: 10.1002/iid3.815. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 36988251 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 1 receptor associated kinase 1 gene polymorphism association with risk of rheumatological diseases in Egyptian population.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jan 18;52(1):135. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10223-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39826020
-
Jieduquyuziyin Prescription Suppresses Inflammatory Activity of MRL/lpr Mice and Their Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages via Inhibiting Expression of IRAK1-NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 14;11:1049. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01049. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32760274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carli L., Tani C., Querci F., et al. Analysis of the prevalence of cataracts and glaucoma in systemic lupus erythematosus and evaluation of the rheumatologists’ practice for the monitoring of glucocorticoid eye toxicity. Clinical Rheumatology. 2013;32(7):1071–1073. doi: 10.1007/s10067-013-2214-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li R. Q., Liu W. H., Hou X. L., et al. Effect of jiedu quyu ziyin decoction on MeCP2 of CD4+ T cells in MRL/lpr lupus mice. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2018;59(4):321–324.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

