Alcohol Intake and Abnormal Expression of Brf1 in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 31781337
- PMCID: PMC6874981
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/4818106
Alcohol Intake and Abnormal Expression of Brf1 in Breast Cancer
Abstract
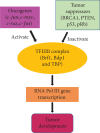
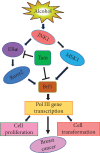
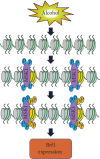
Breast cancer is the most common malignant disease of females. Overall, one woman in every nine will get breast cancer at some time in her life. Epidemiological studies have indicated that alcohol consumption has most consistently been associated with breast cancer risk. However, the mechanism of alcohol-associated breast cancer remains to be addressed. Little is known about the effects of alcohol consumption on Brf1 (TFIIIB-related factor 1) expression and RNA Pol III gene (RNA polymerase III-dependent gene) transcription, which are responsible for protein synthesis and tightly linked to cell proliferation, cell transformation, and tumor development. Emerging evidences have indicated that alcohol induces deregulation of Brf1 and Pol III genes to cause the alterations of cell phenotypes and tumor formation. In this paper, we summarize the progresses regarding alcohol-caused increase in the expression of Brf1 and Pol III genes and analysis of its molecular mechanism of breast cancer. As the earlier and accurate diagnosis approach of breast cancer is not available yet, exploring the molecular mechanism and identifying the biomarker of alcohol-associated breast cancer are especially important. Recent studies have demonstrated that Brf1 is overexpressed in most ER+ (estrogen receptor positive) cases of breast cancer and the change in cellular levels of Brf1 reflects the therapeutic efficacy and prognosis of this disease. It suggests that Brf1 may be a potential diagnosis biomarker and a therapeutic target of alcohol-associated breast cancer.
Copyright © 2019 Chenghao Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tamoxifen represses alcohol-induced transcription of RNA polymerase III-dependent genes in breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2014 Dec 15;5(23):12410-7. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2678. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25400119 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring a common mechanism of alcohol-induced deregulation of RNA Pol III genes in liver and breast cells.Gene. 2017 Aug 30;626:309-318. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.05.048. Epub 2017 May 25. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28552569 Free PMC article.
-
The significance of Runx2 mediating alcohol-induced Brf1 expression and RNA Pol III gene transcription.Chem Biol Interact. 2020 May 25;323:109057. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109057. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 32198086 Free PMC article.
-
ROS Signaling-Mediated Novel Biological Targets: Brf1 and RNA Pol III Genes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Oct 4;2021:5888432. doi: 10.1155/2021/5888432. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9890237. doi: 10.1155/2024/9890237. PMID: 34646425 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Prognostic value and clinicopathological significance of serum- and tissue-based cytokeratin 18 express level in breast cancer: a meta-analysis.Biosci Rep. 2018 Mar 21;38(2):BSR20171145. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171145. Print 2018 Apr 27. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29437899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
BDP1 Alterations Correlate with Clinical Outcomes in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 25;14(7):1658. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071658. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406430 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol Consumption and Breast and Ovarian Cancer Development: Molecular Pathways and Mechanisms.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Dec 20;46(12):14438-14452. doi: 10.3390/cimb46120866. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39727994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitogen- and Stress-Activated Protein Kinase 1 Mediates Alcohol-Upregulated Transcription of Brf1 and tRNA Genes to Cause Phenotypic Alteration.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jun 27;2020:2067959. doi: 10.1155/2020/2067959. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32685086 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer-associated SNP rs72755295 is a cis-regulatory variation for human EXO1.Genet Mol Biol. 2022 Oct 10;45(4):e20210420. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2021-0420. eCollection 2022. Genet Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36255267 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Factors and Breast Cancer Prognosis among Breast Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 23;13(21):5329. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215329. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Alcohol, tobacco and breast cancer - collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 53 epidemiological studies, including 58 515 women with breast cancer and 95 067 women without the disease. British Journal of Cancer. 2002;87(11):1234–1245. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600596. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

