Protective Effects of Garlic and Cinnamon Oils on Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Albino Rats
- PMID: 31781479
- PMCID: PMC6855081
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9895485
Protective Effects of Garlic and Cinnamon Oils on Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Albino Rats
Abstract
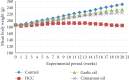
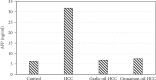
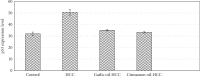
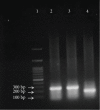
Natural oils are traditional medicinal herbs, which have attracted interests for its potential anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities. The present work is aimed at evaluating the protective effect of garlic oil and cinnamon oil on diethylnitrosamine- (DENA-) and 2-acetylaminofluorene- (2-AAF-) induced p53 gene mutation and hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Forty male albino rats were divided into 4 equal groups: control, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), garlic oil-HCC, and cinnamon oil-HCC. The HCC-induced group showed a significant decrease in the body mass and a significant elevation in the liver weight, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), liver enzymes, hepatic malondialdehyde (MDA), and p53 protein expression levels as well as genetic mutations in intron 5 of p53 gene in the form of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertions. In addition, the glutathione (GSH) level and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities were increased. While HCC rats pretreated with garlic oil or cinnamon oil were significantly reversed, these destructive actions increased GSH and SOD levels. The HCC-induced group showed histopathological features of liver cancer including hypercellularity, nuclear hyperchromasia, mitotic figures, and preneoplastic foci. On the other hand, HCC rats pretreated with garlic oil or cinnamon oil revealed partial reversal of normal liver architecture. The present findings proposed that these natural oils have the ability to improve liver function, significantly reduced the liver toxicity and HCC development. However, further sophisticated studies are recommended before their use as conventional therapeutics for HCC treatment.
Copyright © 2019 Salah M. Aly et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper and no significant competing financial, professional, or personal interests that might have influenced the performance or presentation of the work described in this manuscript.
Figures


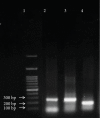
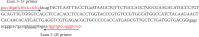
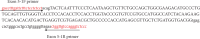




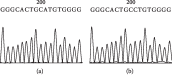





Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effects of curcumin against diethyl nitrosamine induced hepatotoxicity in albino rats.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(1):103-8. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.1.103. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25640336
-
Chemosensitizing effect of Alpinia officinarum rhizome extract in cisplatin-treated rats with hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:710-718. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.128. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29524879
-
Anti-cancer effects of Ajwa dates (Phoenix dactylifera L.) in diethylnitrosamine induced hepatocellular carcinoma in Wistar rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Aug 22;17(1):418. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1926-6. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28830415 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of garlic extract against hematological alterations, immunosuppression, hepatic oxidative stress, and renal damage induced by cyclophosphamide in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 May;26(15):15559-15572. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04993-7. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30945076
-
Cinnamon and Eucalyptus Oils Suppress the Inflammation Induced by Lipopolysaccharide In Vivo.Molecules. 2021 Dec 6;26(23):7410. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237410. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34885991 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant Phytoconstituents From Onosma bracteata Wall. (Boraginaceae) Ameliorate the CCl4 Induced Hepatic Damage: In Vivo Study in Male Wistar Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 21;11:1301. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01301. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32973525 Free PMC article.
-
Cinnamaldehyde: Pharmacokinetics, anticancer properties and therapeutic potential (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 Sep;30(3):163. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13287. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38994757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cinnamon oil solid self-microemulsion mediates chronic mild stress-induced depression in mice by modulating monoamine neurotransmitters, corticosterone, inflammation cytokines, and intestinal flora.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 22;9(6):e17125. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17125. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37416658 Free PMC article.
-
The chemoprevention of spirulina platensis and garlic against diethylnitrosamine induced liver cancer in rats via amelioration of inflammatory cytokines expression and oxidative stress.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021 Dec 4;11(1):22-31. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfab118. eCollection 2022 Feb. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 35237408 Free PMC article.
-
Montelukast alleviates thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May 24. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04291-9. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40411618
References
-
- Roy S. R., Gadad P. C. Effect of β-asarone on diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Indian Journal of Health Sciences and Biomedical Research (KLEU) 2016;9(1):p. 82. doi: 10.4103/2349-5006.183687. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

