The Induction of a Permissive Environment to Promote T Cell Immune Evasion in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: The Metabolic Perspective
- PMID: 31781489
- PMCID: PMC6851227
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01166
The Induction of a Permissive Environment to Promote T Cell Immune Evasion in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: The Metabolic Perspective
Abstract
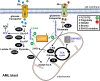
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the acute leukemia with highest incidence amongst adults. Despite significant improvements in understanding the genomic landscape and the introduction of novel drugs, long-term outcome remains unsatisfactory. Recently, immunotherapeutic approaches have heralded a new era in cancer treatment. The success of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in AML highlights the disease's immunoresponsiveness. Several immunotherapeutic applications are currently under clinical evaluation and include immune checkpoint blockades, T cell-engaging antibodies, and genetically engineered T cells. However, immunoevasive mechanisms employed by AML blasts severely hamper our endeavors. A better understanding of the underlying mechanisms remains a prerequisite for improving treatment efficacy. One of the hallmarks of the cancer cells is metabolic reprogramming, introduced by Otto Warburg's seminal studies during the beginnings of the last century. Nowadays, it is well established that metabolic adaptation is not just an epiphenomenon during oncogenesis but rather a necessity for tumor development and progression. Furthermore, accumulating data suggest an important role of aberrant tumor cell metabolism for immune escape. AML blasts display a number of metabolic alterations that could be linked to immunoregulation, and these include competition over substrates, abundant release of bioactive metabolites, and an overall microenvironmental metabolic re-modeling that favors the induction or survival of immunoregulatory cell subsets such as regulatory T cells. In this review, we outline the immunoevasive character of the AML blasts' bioenergetics, set it into context with oncogenic mutations, and discuss potentially suitable countermeasures and their limitations.
Keywords: AML—acute myeloid leukemia; immunoescape mechanisms; immunotherapy; microenvironment; tumor metabolism.
Copyright © 2019 Mougiakakos.
Figures


References
-
- Krupka C, Kufer P, Kischel R, Zugmaier G, Lichtenegger FS, Kohnke T, et al. . Blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis augments lysis of AML cells by the CD33/CD3 BiTE antibody construct AMG 330: reversing a T-cell-induced immune escape mechanism. Leukemia. (2016) 30:484–91. 10.1038/leu.2015.214 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

