Epithelial Mesenchymal and Endothelial Mesenchymal Transitions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review
- PMID: 31781608
- PMCID: PMC6855070
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/2962580
Epithelial Mesenchymal and Endothelial Mesenchymal Transitions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review
Abstract
Purpose: To present a comprehensive review of the literature data, published between 2000 and 2019 on the PubMed and Web of Science databases, in the field of the tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). All the data were combined with the personal experiences of the authors.
Design: From 1002 representative papers, we selected 86 representative publications which included data on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), angiogenesis, cancer stem-like cells (CSCs), and molecular background of chemoresistance or resistance to radiotherapy.
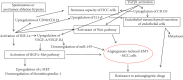
Results: Although the central event concerns activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, other signal pathways, such as c-Met/HGF/Snail, Notch-1/NF-κB, TGF-β/SMAD, and basic fibroblast growth factor-related signaling, play a role in the EMT of HCC cells. This pathway is targeted by specific miRNAs and long noncoding RNAs, as explored in this paper. A central player in the tumor microenvironment proved to be the CSCs which can be marked by CD133, CD44, CD90, EpCAM, and CD105. CSCs can induce resistance to cytotoxic therapy or, alternatively, can be synthesized, de novo, after chemo- or radiotherapy, especially after transarterial chemoembolization- or radiofrequency ablation-induced hypoxia. The circulating tumor cells proved to have epithelial, intermediate, or mesenchymal features; their properties have a critical prognostic role.
Conclusion: The metastatic pathway of HCC seems to be related to the Wnt- or, rather, TGFβ1-mediated inflammation-angiogenesis-EMT-CSCs crosstalk link. Molecular therapy should target this molecular axis controlling the HCC microenvironment.
Copyright © 2019 Simona Gurzu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibitions of epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells-like properties are involved in miR-148a-mediated anti-metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Carcinog. 2014 Dec;53(12):960-9. doi: 10.1002/mc.22064. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Mol Carcinog. 2014. PMID: 23861222
-
Updates on the hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met axis in hepatocellular carcinoma and its therapeutic implications.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Sep 7;24(33):3695-3708. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i33.3695. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30197476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of VEGFR-2 inhibitors exerting significant anticancer activity against CD44+ and CD133+ cancer stem cells (CSCs): Reversal of TGF-β induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Dec 1;207:112851. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112851. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 33002846
-
Transforming growth factor-β-induced plasticity causes a migratory stemness phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2017 Apr 28;392:39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.01.037. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28161507
-
Regulation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Mechanism and Targeted Therapeutic Approaches.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1450:93-102. doi: 10.1007/5584_2023_781. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 37452258 Review.
Cited by
-
EFNA5 suppresses cell proliferation and tumor metastasis in hepatoma via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Discov Oncol. 2024 Oct 19;15(1):572. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01454-7. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39424684 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Novel Nilotinib Analogues and Biological Evaluation of Their Antiplatelet Activity and Functionality towards Cancer Cell Proliferation In Vitro.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Mar 7;17(3):349. doi: 10.3390/ph17030349. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543136 Free PMC article.
-
Development and External Validation of a Novel Immune Checkpoint-Related Gene Signature for Prediction of Overall Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jan 21;7:620765. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.620765. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33553243 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating tumor cell markers for early detection and drug resistance assessment through liquid biopsy.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 7;15:1494723. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1494723. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40260304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Down-Regulated CMTM2 Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jun 17;13:5731-5741. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S250370. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32606785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mao X., Zhang Y., Lin N. Application and perspectives of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of liver cancer. Cancer Translational Medicine. 2015;1(3):101–107. doi: 10.4103/2395-3977.159538. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

