A Rationale for Allopregnanolone Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorders: Basic and Clinical Studies
- PMID: 31782169
- PMCID: PMC7018555
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.14253
A Rationale for Allopregnanolone Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorders: Basic and Clinical Studies
Abstract
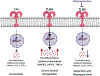
For many years, research from around the world has suggested that the neuroactive steroid (3α,5α)-3-hydroxypregnan-20-one (allopregnanolone or 3α,5α-THP) may have therapeutic potential for treatment of various symptoms of alcohol use disorders (AUDs). In this critical review, we systematically address all the evidence that supports such a suggestion, delineate the etiologies of AUDs that are addressed by treatment with allopregnanolone or its precursor pregnenolone, and the rationale for treatment of various components of the disease based on basic science and clinical evidence. This review presents a theoretical framework for understanding how endogenous steroids that regulate the effects of stress, alcohol, and the innate immune system could play a key role in both the prevention and the treatment of AUDs. We further discuss cautions and limitations of allopregnanolone or pregnenolone therapy with suggestions regarding the management of risk and the potential for helping millions who suffer from AUDs.
Keywords: Allopregnanolone; Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Signaling; GABA Inhibition; Neuroactive Steroid; Neuroimmune Signaling.
© 2019 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures



References
-
- Adinoff B, Martin PR, Bone GH, Eckardt MJ, Roehrich L, George DT, Moss HB, Eskay R, Linnoila M, Gold PW (1990) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis functioning and cerebrospinal fluid corticotropin releasing hormone and corticotropin levels in alcoholics after recent and long-term abstinence. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 47:325–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

