Ectopic Posterior Pituitary, Polydactyly, Midfacial Hypoplasia and Multiple Pituitary Hormone Deficiency due to a Novel Heterozygous IVS11-2A>C(c.1957-2A>C) Mutation in the GLI2 Gene
- PMID: 31782289
- PMCID: PMC7499131
- DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2019.2019.0142
Ectopic Posterior Pituitary, Polydactyly, Midfacial Hypoplasia and Multiple Pituitary Hormone Deficiency due to a Novel Heterozygous IVS11-2A>C(c.1957-2A>C) Mutation in the GLI2 Gene
Abstract
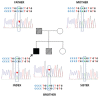
A novel heterozygous IVS11-2A>C(c.1957-2A>C) mutation in the GLI2 gene is reported. There was an extremely distinct phenotypical expression in two siblings and their father. The index case was a boy who developed cholestasis and hypoglycaemia in the neonatal period. He had bilateral postaxial polydactyly, mid-facial hypoplasia, high palatal arch, micropenis, and bilateral cryptorchidism. Laboratory examination revealed a diagnosis of multiple pituitary hormone deficiency. There was severe anterior pituitary hypoplasia, absent pituitary stalk and ectopic posterior pituitary on magnetic resonance imaging which suggested pituitary stalk interruption syndrome with no other midline structural abnormality. Molecular genetic analysis revealed a novel heterozygous splicing IVS11-2A>C(c.1957-2A>C) mutation detected in the GLI2 gene. His father and a six-year-old brother with the identical mutation also had unilateral postaxial polydactyly and mid-facial hypoplasia although there was no pituitary hormone deficiency. This novel heterozygous GLI2 mutation detected appears to present with an extremely variable clinical phenotype, even in related individuals with an identical mutation, suggesting incomplete penetrance of this GLI2 mutation.
Keywords: Growth hormone deficiency; polydactyly; GLI2 mutations; multiple pituitary hormone deficiency.
Figures

References
-
- França MM, Jorge AA, Carvalho LR, Costalonga EF, Vasques GA, Leite CC, Mendonca BB, Arnhold IJ. Novel heterozygous nonsense GLI2 mutations in patients with hypopituitarism and ectopic posterior pituitary lobe without holoprosencephaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:384–391. - PubMed
-
- Shirakawa T, Nakashima Y, Watanabe S, Harada S, Kinoshita M, Kihara T, Hamasaki Y, Shishido S, Yoshiura KI, Moriuchi H, Dateki S. A novel heterozygous GLI2 mutation in a patient with congenital urethral stricture and renal hypoplasia/dysplasia leading to end-stage renal failure. CEN Case Rep. 2018;7:94–97. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bear KA, Solomon BD, Antonini S, Arnhold IJ, França MM, Gerkes EH, Grange DK, Hadley DW, Jääskeläinen J, Paulo SS, Rump P, Stratakis CA, Thompson EM, Willis M, Winder TL, Jorge AA, Roessler E, Muenke M. Pathogenic mutations in GLI2 cause a specific phenotype that is distinct from holoprosencephaly. J Med Genet. 2014;51:413–418. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
