UHRF1 downmodulation enhances antitumor effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors in retinoblastoma by augmenting oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 31782885
- PMCID: PMC6998393
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12607
UHRF1 downmodulation enhances antitumor effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors in retinoblastoma by augmenting oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis
Abstract
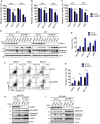
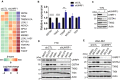
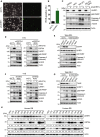
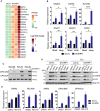
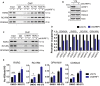
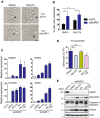
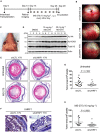
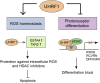
Identification of new genetic pathways or molecular targets that sensitize cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs may improve the efficacy of current chemotherapy. Here, we report that downmodulation of UHRF1 (ubiquitin-like with PHD and RING finger domains 1) in retinoblastoma (RB) cells increases the sensitivity to histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, augmenting apoptotic cell death. We found that UHRF1 depletion downregulates two redox-responsive genes GSTA4 (glutathione S-transferase α4) and TXN2 (thioredoxin-2) in RB cells, and increases the basal level of intracellular oxidative stress. Antioxidant treatment significantly reduced both basal and HDAC inhibitor-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in UHRF1-depleted cells. Knockdown of GSTA4 or TXN2 sensitized RB cells to HDAC inhibitors, demonstrating that GSTA4 and TXN2 play key roles in redox homeostasis in RB cells and the susceptibility to HDAC inhibitor treatment upon UHRF1 depletion. In human primary RB, GSTA4 and TXN2 proteins were found to be mostly elevated along with high UHRF1 expression. In addition to augmentation of apoptosis in UHRF1-depleted RB cells, we also show that UHRF1 downmodulation derepresses the expression of photoreceptor-specific genes in RB cells in cooperation with a HDAC inhibitor MS-275 and promotes neuron-like differentiation. However, further investigation revealed that the enhanced growth-inhibitory effects of MS-275 in UHRF1-depleted cells were still mainly due to robust apoptosis induction rather than differentiation-mediated growth arrest. Consistent with our findings, UHRF1 depletion in RB cells increased the therapeutic efficacy of MS-275 in murine orthotopic xenografts. These results provide a novel basis for potential benefits of UHRF1 targeting for RB treatment.
Keywords: HDAC inhibitors; UHRF1; chemotherapy; drug sensitivity; retinoblastoma.
© 2019 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
UHRF1 depletion sensitizes retinoblastoma cells to chemotherapeutic drugs via downregulation of XRCC4.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Feb 7;9(2):164. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0203-4. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29415984 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing UHRF1 Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Promotes Cell Apoptosis in Retinoblastoma Via the PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Apr;26(2):1079-1088. doi: 10.1007/s12253-019-00656-7. Epub 2019 May 2. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 31044388
-
Chromatin remodelers HELLS and UHRF1 mediate the epigenetic deregulation of genes that drive retinoblastoma tumor progression.Oncotarget. 2014 Oct 30;5(20):9594-608. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2468. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25338120 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin regulators in retinoblastoma: Biological roles and therapeutic applications.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Apr;236(4):2318-2332. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30022. Epub 2020 Aug 25. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32840881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Down-regulation of UHRF1, associated with re-expression of tumor suppressor genes, is a common feature of natural compounds exhibiting anti-cancer properties.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Apr 15;30(1):41. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-41. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21496237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thioredoxin (Trx): A redox target and modulator of cellular senescence and aging-related diseases.Redox Biol. 2024 Apr;70:103032. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103032. Epub 2024 Jan 13. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38232457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-141-3p promotes retinoblastoma progression via inhibiting sushi domain-containing protein 2.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):7410-7424. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2048770. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35259051 Free PMC article.
-
Curzerene suppresses progression of human glioblastoma through inhibition of glutathione S-transferase A4.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 May;28(5):690-702. doi: 10.1111/cns.13800. Epub 2022 Jan 20. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 35048517 Free PMC article.
-
atm Mutation and Oxidative Stress Enhance the Pre-Cancerous Effects of UHRF1 Overexpression in Zebrafish Livers.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 14;15(8):2302. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082302. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190230 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of UHRF1 Promotes PINK1-mediated Mitophagy to Alleviates Ferroptosis in Diabetic Nephropathy.Inflammation. 2024 Apr;47(2):718-732. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01940-0. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 38055118
References
-
- Bronner C, Krifa M and Mousli M (2013) Increasing role of UHRF1 in the reading and inheritance of the epigenetic code as well as in tumorogenesis. Biochem Pharmacol 86, 1643–1649. - PubMed
-
- Chan HS, Gallie BL, Munier FL and Beck Popovic M (2005) Chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. Ophthalmol Clin North Am 18, 55–63, viii. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

