Restriction factors in human retrovirus infections and the unprecedented case of CIITA as link of intrinsic and adaptive immunity against HTLV-1
- PMID: 31783769
- PMCID: PMC6884849
- DOI: 10.1186/s12977-019-0498-6
Restriction factors in human retrovirus infections and the unprecedented case of CIITA as link of intrinsic and adaptive immunity against HTLV-1
Abstract
Background: Immunity against pathogens evolved through complex mechanisms that only for sake of simplicity are defined as innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Indeed innate and adaptive immunity are strongly intertwined each other during evolution. The complexity is further increased by intrinsic mechanisms of immunity that rely on the action of intracellular molecules defined as restriction factors (RFs) that, particularly in virus infections, counteract the action of pathogen gene products acting at different steps of virus life cycle.
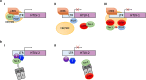
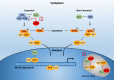
Main body and conclusion: Here we provide an overview on the nature and the mode of action of restriction factors involved in retrovirus infection, particularly Human T Leukemia/Lymphoma Virus 1 (HTLV-1) infection. As it has been extensively studied by our group, special emphasis is given to the involvement of the MHC class II transactivator CIITA discovered in our laboratory as regulator of adaptive immunity and subsequently as restriction factor against HIV-1 and HTLV-1, a unique example of dual function linking adaptive and intrinsic immunity during evolution. We describe the multiple molecular mechanisms through which CIITA exerts its restriction on retroviruses. Of relevance, we review the unprecedented findings pointing to a concerted action of several restriction factors such as CIITA, TRIM22 and TRIM19/PML in synergizing against retroviral replication. Finally, as CIITA profoundly affects HTLV-1 replication by interacting and inhibiting the function of HTLV-1 Tax-1 molecule, the major viral product associated to the virus oncogenicity, we also put forward the hypothesis of CIITA as counteractor of HTLV-1-mediated cancer initiation.
Keywords: CIITA; HIV; HTLV-1; Intrinsic immunity; Restriction factors; Tax.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Transactivator CIITA Inhibits the Persistent Activation of NF-κB by the Human T Cell Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 Tax-1 Oncoprotein.J Virol. 2016 Jan 20;90(7):3708-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03000-15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26792751 Free PMC article.
-
The MHC-II transactivator CIITA, a restriction factor against oncogenic HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 retroviruses: similarities and differences in the inhibition of Tax-1 and Tax-2 viral transactivators.Front Microbiol. 2013 Aug 22;4:234. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00234. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23986750 Free PMC article.
-
Major histocompatibility complex class II transactivator CIITA is a viral restriction factor that targets human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax-1 function and inhibits viral replication.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(20):10719-29. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00813-11. Epub 2011 Aug 3. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21813598 Free PMC article.
-
The dual function of the MHC class II transactivator CIITA against HTLV retroviruses.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(11):4149-56. doi: 10.2741/3519. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19273341 Review.
-
Tripartite Motif 22 and Class II Transactivator Restriction Factors: Unveiling Their Concerted Action against Retroviruses.Front Immunol. 2017 Oct 18;8:1362. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01362. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29093716 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The NLR member CIITA: Master controller of adaptive and intrinsic immunity and unexpected tool in cancer immunotherapy.Biomed J. 2023 Oct;46(5):100631. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.100631. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Biomed J. 2023. PMID: 37467968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host Restriction Factors Modulating HIV Latency and Replication in Macrophages.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 11;23(6):3021. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063021. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bovine Leukemia Virus and Human Breast Cancer: A Review of Clinical and Molecular Evidence.Viruses. 2025 Feb 26;17(3):324. doi: 10.3390/v17030324. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40143252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The viral protein U (Vpu)-interacting host protein ATP6V0C down-regulates cell-surface expression of tetherin and thereby contributes to HIV-1 release.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 22;295(21):7327-7340. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013280. Epub 2020 Apr 14. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32291285 Free PMC article.
-
The helicase-like transcription factor redirects the autophagic flux and restricts human T cell leukemia virus type 1 infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug;120(31):e2216127120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2216127120. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37487091 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

