1α, 25-dihydroxy Vitamin D3 containing fractions of Catharanthus roseus leaf aqueous extract inhibit preadipocyte differentiation and induce lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells
- PMID: 31783835
- PMCID: PMC6883588
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-019-2754-7
1α, 25-dihydroxy Vitamin D3 containing fractions of Catharanthus roseus leaf aqueous extract inhibit preadipocyte differentiation and induce lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells
Abstract
Background: To investigate the potential of Catharanthus roseus leaf aqueous crude extract (CRACE) as a regulator of adipocyte development and function.
Methods: 3T3-L1 adipogenesis model was used to investigate the effect of CRACE on adipogenesis. 3T3-L1 preadipocytes (for adipogenic differentiation) and mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes (for adipocyte function) were treated with non-toxic doses of CRACE. The outcomes were corroborated by intracellular lipid accumulation, expression of pro-and anti-adipogenic effector molecules. To investigate CRACE mediated lipolysis, cAMP accumulation, glycerol release and phosphorylation of key effector molecules were tested in treated mature adipocytes. Finally, the extract was fractionated to identify the active molecule/s in the extract.
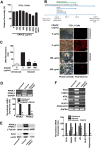
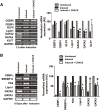
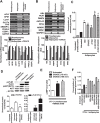
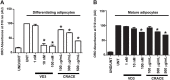
Results: CRACE significantly reduced adipocyte differentiation by modulating PPARγ expression. At early stage CRACE directly targeted Lipin1 expression and consequently impacted KLF7, subsequently expression of GATA2, CEBPα, SREBP1c were targeted, with PPARγ expression, particularly curtailed. While CRACE significantly reduced several lipogenic genes like FAS and GPD1 in mature adipocytes, concomitantly, it greatly increased lipolysis resulting in decreased lipid accumulation in mature adipocytes. The increase in lipolysis was due to decreased Akt activation, increased cAMP level, and PKA activity. The fractionation of CRACE allowed identification of two fractions with potent anti-adipogenic activity. Both the fractions contained 1α, 25-dihydroxy Vitamin D3 as major component.
Conclusions: 1α, 25-dihydroxy Vitamin D3 containing CRACE can be developed into an effective anti-obesity formulation that decreases adipogenesis and increases lipid catabolism.
Keywords: 3T3-L1; Adipogenesis; Catharanthus roseus; Lipolysis; Obesity; Vitamin D3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
APPL1 knockdown blocks adipogenic differentiation and promotes adipocyte lipolysis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020 Apr 15;506:110755. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.110755. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32045627
-
AZD1208, a pan-Pim kinase inhibitor, inhibits adipogenesis and induces lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Apr;22(4):2488-2497. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13559. Epub 2018 Feb 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29441719 Free PMC article.
-
Korean Chungtaejeon tea extract attenuates body weight gain in C57BL/6J-Lep ob/ob mice and regulates adipogenesis and lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.J Integr Med. 2017 Jan;15(1):56-63. doi: 10.1016/S2095-4964(17)60321-2. J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 28088260
-
Glycine enhances expression of adiponectin and IL-10 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes without affecting adipogenesis and lipolysis.Amino Acids. 2018 May;50(5):629-640. doi: 10.1007/s00726-018-2537-3. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Amino Acids. 2018. PMID: 29356901
-
In vitro effects of phytochemicals on adipogenesis with a focus on molecular mechanisms: A systematic review.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(4):409-425. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.78924.17090. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39968092 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular function of Krüppel-like factor 7 in biology.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023 May 24;55(5):713-725. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023061. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023. PMID: 37227154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of chitinase genes in tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) under biotic stress conditions.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2021 Feb;27(2):369-385. doi: 10.1007/s12298-021-00947-x. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2021. PMID: 33707875 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

