Antitumor and antioxidant effects of Clinacanthus nutans Lindau in 4 T1 tumor-bearing mice
- PMID: 31783838
- PMCID: PMC6884788
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-019-2757-4
Antitumor and antioxidant effects of Clinacanthus nutans Lindau in 4 T1 tumor-bearing mice
Abstract
Background: Clinacanthus nutans Lindau (C. nutans) is a species of in Acanthaceae family and primarily used in South East Asian countries. C. nutans is well known as Sabah snake grass in Malaysia, and its leaves have diverse medicinal potential in conventional applications, including cancer treatments. On the basis of literature search, there is less conclusive evidence of the involvement of phytochemical constituents in breast cancer, in particular, animal tumor models. The current study aimed to determine the antitumor and antioxidant activities of C. nutans extract in 4 T1 tumor-bearing mice.
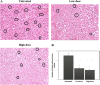
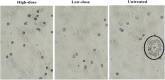
Methods: C. nutans leaves were subjected to methanol extraction and divided into two different concentrations, 200 mg/kg (low-dose) and 1000 mg/kg (high-dose). The antitumor effects of C. nutans extracts were assessed using bone marrow smearing, clonogenic, and splenocyte immunotype analyses. In addition, hematoxylin and eosin, tumor weight and tumor volume profiles also used to indicate apoptosis appearance. Serum cytokine levels were examined using ELISA assay. In addition, nitric oxide assay reflecting antioxidant activity was performed.
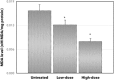
Results: From the results obtained, the methanol extract of C. nutans leaves at 200 mg/kg (P < 0.05) and 1000 mg/kg (P < 0.05) showed a significant decrease in nitric oxide (NO) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in the blood. On the other hand, C. nutans extract (1000 mg/kg) also showed a significant decrease in the number of mitotic cells, tumor weight, and tumor volume. No inflammatory and adverse reactions related to splenocytes activities were found in all treated groups of mice. Despite its promising results, the concentration of both C. nutans extracts have also reduced the number of colonies formed in the liver and lungs.
Conclusion: In conclusion, C. nutans extracts exert antitumor and antioxidant activities against 4 T1 mouse breast model with no adverse effect and inflammatory response at high dose of 1000 mg/kg, indicating an effective and complementary approach for cancer prevention and treatment.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Antitumor; Breast tumor; Clinacanthus nutans Lindau.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cytotoxicity and cytochrome P450 inhibitory activities of Clinacanthus nutans.Drug Metab Pers Ther. 2017 Mar 1;32(1):59-65. doi: 10.1515/dmpt-2016-0034. Drug Metab Pers Ther. 2017. PMID: 28253196
-
Comparison of cytotoxicity between extracts of Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau leaves from different locations and the induction of apoptosis by the crude methanol leaf extract in D24 human melanoma cells.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Sep 20;16:368. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1348-x. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27646974 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnopharmacological uses, phytochemistry, biological activities, and therapeutic applications of Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau: A comprehensive review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jul 12;206:245-266. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28495603 Review.
-
Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau Ethanol Extract Inhibits Hepatoma in Mice through Upregulation of the Immune Response.Molecules. 2015 Sep 18;20(9):17405-28. doi: 10.3390/molecules200917405. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26393569 Free PMC article.
-
A Narrative Review on the Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Therapeutic Potentials of Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau Leaves as an Alternative Source of Future Medicine.Molecules. 2021 Dec 27;27(1):139. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010139. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Activities of Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 28;24(13):10789. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310789. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in Herbage Yield, Antioxidant Activities, Phytochemical Contents, and Bioactive Compounds of Sabah Snake Grass (Clinacanthus Nutans L.) with Regards to Harvesting Age and Harvesting Frequency.Molecules. 2020 Jun 19;25(12):2833. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122833. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32575450 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Approach for Rapid Identification of Antioxidants in Clinacanthus nutans Leaves with Liver Protective Potential.Molecules. 2022 Jun 7;27(12):3650. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123650. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744776 Free PMC article.
-
Clinacanthus nutans Mitigates Neuronal Death and Reduces Ischemic Brain Injury: Role of NF-κB-driven IL-1β Transcription.Neuromolecular Med. 2021 Mar;23(1):199-210. doi: 10.1007/s12017-020-08618-y. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Neuromolecular Med. 2021. PMID: 33025396
-
Crosstalk between fatty acid metabolism and tumour-associated macrophages in cancer progression.Biomedicine (Taipei). 2022 Dec 1;12(4):9-19. doi: 10.37796/2211-8039.1381. eCollection 2022. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2022. PMID: 36816174 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Syed Najmuddin SUF, Alitheen NB, Hamid M, Nik Abd Rahman NMA. Comparative study of antioxidant level and activity from leaf extracts of Annona muricata linn obtained from different locations. Pertanika J Trop Agric Sci. 2017;40:119–130.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

