The Paf1 complex and P-TEFb have reciprocal and antagonist roles in maintaining multipotent neural crest progenitors
- PMID: 31784460
- PMCID: PMC6955205
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.180133
The Paf1 complex and P-TEFb have reciprocal and antagonist roles in maintaining multipotent neural crest progenitors
Abstract
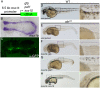
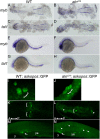
Multipotent progenitor populations are necessary for generating diverse tissue types during embryogenesis. We show the RNA polymerase-associated factor 1 complex (Paf1C) is required to maintain multipotent progenitors of the neural crest (NC) lineage in zebrafish. Mutations affecting each Paf1C component result in near-identical NC phenotypes; alyron mutant embryos carrying a null mutation in paf1 were analyzed in detail. In the absence of zygotic paf1 function, definitive premigratory NC progenitors arise but fail to maintain expression of the sox10 specification gene. The mutant NC progenitors migrate aberrantly and fail to differentiate appropriately. Blood and germ cell progenitor development is affected similarly. Development of mutant NC could be rescued by additional loss of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) activity, a key factor in promoting transcription elongation. Consistent with the interpretation that inhibiting/delaying expression of some genes is essential for maintaining progenitors, mutant embryos lacking the CDK9 kinase component of P-TEFb exhibit a surfeit of NC progenitors and their derivatives. We propose Paf1C and P-TEFb act antagonistically to regulate the timing of the expression of genes needed for NC development.
Keywords: Neural crest; P-TEFb; Paf1 complex; Stem cells; Transcription pausing; Zebrafish mutant.
© 2019. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The positive transcriptional elongation factor (P-TEFb) is required for neural crest specification.Dev Biol. 2016 Aug 15;416(2):361-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.06.012. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27343897
-
Neural crest survival and differentiation in zebrafish depends on mont blanc/tfap2a gene function.Development. 2004 Apr;131(7):1463-77. doi: 10.1242/dev.01033. Epub 2004 Feb 25. Development. 2004. PMID: 14985255
-
A systems biology approach uncovers the core gene regulatory network governing iridophore fate choice from the neural crest.PLoS Genet. 2018 Oct 4;14(10):e1007402. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007402. eCollection 2018 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30286071 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of the neural crest state: control of stem cell attributes by gene regulatory, post-transcriptional and epigenetic interactions.Dev Biol. 2012 Jun 1;366(1):10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.03.014. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22583479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The issue of the multipotency of the neural crest cells.Dev Biol. 2018 Dec 1;444 Suppl 1:S47-S59. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.03.024. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29614271 Review.
Cited by
-
Rtf1-dependent transcriptional pausing regulates cardiogenesis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 15:2023.10.13.562296. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.13.562296. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37873297 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Rtf1 Transcriptionally Regulates Neonatal and Adult Cardiomyocyte Biology.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 May 20;10(5):221. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10050221. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37233188 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic regulation of enteric nervous system development in zebrafish.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Feb 28;52(1):177-190. doi: 10.1042/BST20230343. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38174765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of rare coding variants to microcephaly in individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders.Genome Med. 2025 Aug 6;17(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13073-025-01513-w. Genome Med. 2025. PMID: 40770811 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated regulation of RNA polymerase II pausing and elongation progression by PAF1.Sci Adv. 2022 Apr;8(13):eabm5504. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm5504. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35363521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelman K., Kennedy M. A., Nechaev S., Gilchrist D. A., Muse G. W., Chinenov Y. and Rogatsky I. (2009). Immediate mediators of the inflammatory response are poised for gene activation through RNA polymerase II stalling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 18207-18212. 10.1073/pnas.0910177106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

