Recycling Waste Circuit Board Efficiently and Environmentally Friendly through Small-Molecule Assisted Dissolution
- PMID: 31784554
- PMCID: PMC6884634
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-54045-w
Recycling Waste Circuit Board Efficiently and Environmentally Friendly through Small-Molecule Assisted Dissolution
Abstract
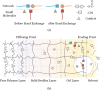
With the increasing amount of electronic waste (e-waste) generated globally, it is an enormous challenge to recycle printed circuit boards (PCBs) efficiently and environmentally friendly. However, conventional recycling technologies have low efficiency and require tough treatment such as high temperature (>200 °C) and high pressure. In this paper, a small-molecule assisted approach based on dynamic reaction was proposed to dissolve thermosetting polymers containing ester groups and recycle electronic components from PCBs. This effective approach operates below 200 °C and the polymer could be dissolved in a short time. It has a remarkable ability to recycle a wide range of commercial PCBs, including boards made of typical anhydride epoxy or polyester substrate. Besides, it is environmentally friendly as even the recycling solution could be reused multiple times. In addition, the wasted solution after recycling could be used for board bonding and damage repair. This work also demonstrates the advantage of using polymers containing ester groups as the PCB substrate in consideration of eco-friendly and efficient recycling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A new approach to designing easily recyclable printed circuit boards.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 23;12(1):22199. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26677-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36564465 Free PMC article.
-
Recycling of waste printed circuit boards: a review of current technologies and treatment status in China.J Hazard Mater. 2009 May 30;164(2-3):399-408. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.08.051. Epub 2008 Aug 23. J Hazard Mater. 2009. PMID: 18829162 Review.
-
Dissolution and separation of non-metallic powder from printed circuit boards by using chloride solvent.Waste Manag. 2021 Mar 15;123:60-68. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2021.01.024. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Waste Manag. 2021. PMID: 33561771
-
An innovative method of recycling metals in printed circuit board (PCB) using solutions from PCB production.J Hazard Mater. 2020 May 15;390:121892. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121892. Epub 2019 Dec 12. J Hazard Mater. 2020. PMID: 31883733
-
Toward environmentally-benign utilization of nonmetallic fraction of waste printed circuit boards as modifier and precursor.Waste Manag. 2015 Jan;35:236-46. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2014.09.020. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Waste Manag. 2015. PMID: 25445263 Review.
Cited by
-
A new approach to designing easily recyclable printed circuit boards.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 23;12(1):22199. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26677-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36564465 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Emerging Polymer Chemistries for the Advancement of Recyclable, Biodegradable, and Biocompatible Electronics.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Jul;8(14):e2101233. doi: 10.1002/advs.202101233. Epub 2021 May 20. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34014619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping Plastic and Plastic Additive Cycles in Coastal Countries: A Norwegian Case Study.Environ Sci Technol. 2024 May 14;58(19):8336-8348. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c09176. Epub 2024 May 4. Environ Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 38703133 Free PMC article.
-
Biolixiviation of Metals from Computer Printed Circuit Boards by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Bioremoval of Metals by Mixed Culture Subjected to a Magnetic Field.Curr Microbiol. 2023 Apr 29;80(6):197. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03307-y. Curr Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37119300
-
Efficient Electrocatalyst Nanoparticles from Upcycled Class II Capacitors.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Aug 5;12(15):2697. doi: 10.3390/nano12152697. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35957128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumar A, Holuszko M, Espinosa DCR. E-waste: An overview on generation, collection, legislation and recycling practices. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017;122:32–42. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.01.018. - DOI
-
- Awasthi AK, Li J, Koh L, Ogunseitan OA. Circular economy and electronic waste. Nature Electronics. 2019;2:86–89. doi: 10.1038/s41928-019-0225-2. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

