Functional maturation of human neural stem cells in a 3D bioengineered brain model enriched with fetal brain-derived matrix
- PMID: 31784595
- PMCID: PMC6884597
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-54248-1
Functional maturation of human neural stem cells in a 3D bioengineered brain model enriched with fetal brain-derived matrix
Abstract
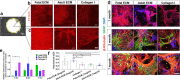
Brain extracellular matrix (ECM) is often overlooked in vitro brain tissue models, despite its instructive roles during development. Using developmental stage-sourced brain ECM in reproducible 3D bioengineered culture systems, we demonstrate enhanced functional differentiation of human induced neural stem cells (hiNSCs) into healthy neurons and astrocytes. Particularly, fetal brain tissue-derived ECM supported long-term maintenance of differentiated neurons, demonstrated by morphology, gene expression and secretome profiling. Astrocytes were evident within the second month of differentiation, and reactive astrogliosis was inhibited in brain ECM-enriched cultures when compared to unsupplemented cultures. Functional maturation of the differentiated hiNSCs within fetal ECM-enriched cultures was confirmed by calcium signaling and spectral/cluster analysis. Additionally, the study identified native biochemical cues in decellularized ECM with notable comparisons between fetal and adult brain-derived ECMs. The development of novel brain-specific biomaterials for generating mature in vitro brain models provides an important path forward for interrogation of neuron-glia interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Bioengineering tissue morphogenesis and function in human neural organoids.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar;111:52-59. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.05.025. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 32540123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid-Bilayer-Supported 3D Printing of Human Cerebral Cortex Cells Reveals Developmental Interactions.Adv Mater. 2020 Aug;32(31):e2002183. doi: 10.1002/adma.202002183. Epub 2020 Jun 14. Adv Mater. 2020. PMID: 32537827
-
Expandable and Rapidly Differentiating Human Induced Neural Stem Cell Lines for Multiple Tissue Engineering Applications.Stem Cell Reports. 2016 Sep 13;7(3):557-570. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.07.017. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Stem Cell Reports. 2016. PMID: 27569063 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-specific extracellular matrix accelerates the formation of neural networks and communities in a neuron-glia co-culture on a multi-electrode array.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 11;9(1):4159. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40128-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30858401 Free PMC article.
-
3D biomaterial models of human brain disease.Neurochem Int. 2021 Jul;147:105043. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105043. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Neurochem Int. 2021. PMID: 33887378 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Brain-Derived Bioscaffolds for Neural Progenitor Cell Culture.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 Jan 17;6(2):320-333. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.2c00232. eCollection 2023 Feb 10. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 36798475 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse engineering human brain evolution using organoid models.Brain Res. 2020 Feb 15;1729:146582. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146582. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31809699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asteroid impact: the potential of astrocytes to modulate human neural networks within organoids.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 22;17:1305921. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1305921. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38075269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modelling the central nervous system: tissue engineering of the cellular microenvironment.Emerg Top Life Sci. 2021 Oct 29;5(4):507-517. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20210245. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34524411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiscale engineering of brain organoids for disease modeling.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024 Jul;210:115344. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2024.115344. Epub 2024 May 27. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024. PMID: 38810702 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

