Interaction with the host: the role of fibronectin and extracellular matrix proteins in the adhesion of Gram-negative bacteria
- PMID: 31784893
- PMCID: PMC7248048
- DOI: 10.1007/s00430-019-00644-3
Interaction with the host: the role of fibronectin and extracellular matrix proteins in the adhesion of Gram-negative bacteria
Abstract
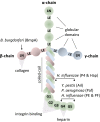
The capacity of pathogenic microorganisms to adhere to host cells and avoid clearance by the host immune system is the initial and most decisive step leading to infections. Bacteria have developed different strategies to attach to diverse host surface structures. One important strategy is the adhesion to extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins (e.g., collagen, fibronectin, laminin) that are highly abundant in connective tissue and basement membranes. Gram-negative bacteria express variable outer membrane proteins (adhesins) to attach to the host and to initiate the process of infection. Understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms of bacterial adhesion is a prerequisite for targeting this interaction by "anti-ligands" to prevent colonization or infection of the host. Future development of such "anti-ligands" (specifically interfering with bacteria-host matrix interactions) might result in the development of a new class of anti-infective drugs for the therapy of infections caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. This review summarizes our current knowledge about the manifold interactions of adhesins expressed by Gram-negative bacteria with ECM proteins and the use of this information for the generation of novel therapeutic antivirulence strategies.
Keywords: Adhesins; Collagen; Extracellular matrix proteins; Fibronectin; Gram-negative bacteria; Laminin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MSCRAMM-mediated adherence of microorganisms to host tissues.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1994;48:585-617. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.48.100194.003101. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 7826020 Review.
-
Identification of an extracellular matrix protein adhesin, EmaA, which mediates the adhesion of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans to collagen.Microbiology (Reading). 2004 Aug;150(Pt 8):2677-2688. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27110-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2004. PMID: 15289564
-
Outer membrane adhesion factor multivalent adhesion molecule 7 initiates host cell binding during infection by gram-negative pathogens.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 12;108(28):11614-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102360108. Epub 2011 Jun 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21709226 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Bartonella henselae with Fibronectin Represents the Molecular Basis for Adhesion to Host Cells.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0059822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00598-22. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35435766 Free PMC article.
-
How bacteria hack the matrix and dodge the bullets of immunity.Eur Respir Rev. 2018 Jun 27;27(148):180018. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0018-2018. Print 2018 Jun 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2018. PMID: 29950304 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The C-terminal head domain of Burkholderia pseudomallei BpaC has a striking hydrophilic core with an extensive solvent network.Mol Microbiol. 2022 Jul;118(1-2):77-91. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14953. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Mol Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35703459 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal capillary basement membrane thickening: Role in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021 May;82:100903. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100903. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 32950677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of virulence-associated factors in Vibrio parahaemolyticus with special reference to moonlighting protein: a secretomics study.Int Microbiol. 2024 Jun;27(3):765-779. doi: 10.1007/s10123-023-00429-y. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Int Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 37702858
-
Incorporation of collagen into Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Burkholderia pseudomallei biofilms enhances their elasticity and resistance against phagocytic clearance.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 27:2023.10.25.564018. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.25.564018. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 37961328 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A tRNA-derived fragment present in E. coli OMVs regulates host cell gene expression and proliferation.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Sep 15;18(9):e1010827. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010827. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36108089 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

