Loss of Oxidation Resistance 1, OXR1, Is Associated with an Autosomal-Recessive Neurological Disease with Cerebellar Atrophy and Lysosomal Dysfunction
- PMID: 31785787
- PMCID: PMC6904826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.11.002
Loss of Oxidation Resistance 1, OXR1, Is Associated with an Autosomal-Recessive Neurological Disease with Cerebellar Atrophy and Lysosomal Dysfunction
Abstract
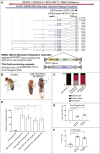
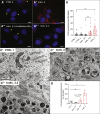
We report an early-onset autosomal-recessive neurological disease with cerebellar atrophy and lysosomal dysfunction. We identified bi-allelic loss-of-function (LoF) variants in Oxidative Resistance 1 (OXR1) in five individuals from three families; these individuals presented with a history of severe global developmental delay, current intellectual disability, language delay, cerebellar atrophy, and seizures. While OXR1 is known to play a role in oxidative stress resistance, its molecular functions are not well established. OXR1 contains three conserved domains: LysM, GRAM, and TLDc. The gene encodes at least six transcripts, including some that only consist of the C-terminal TLDc domain. We utilized Drosophila to assess the phenotypes associated with loss of mustard (mtd), the fly homolog of OXR1. Strong LoF mutants exhibit late pupal lethality or pupal eclosion defects. Interestingly, although mtd encodes 26 transcripts, severe LoF and null mutations can be rescued by a single short human OXR1 cDNA that only contains the TLDc domain. Similar rescue is observed with the TLDc domain of NCOA7, another human homolog of mtd. Loss of mtd in neurons leads to massive cell loss, early death, and an accumulation of aberrant lysosomal structures, similar to what we observe in fibroblasts of affected individuals. Our data indicate that mtd and OXR1 are required for proper lysosomal function; this is consistent with observations that NCOA7 is required for lysosomal acidification.
Keywords: Drosophila; MiMIC; NCOA7; T2A-GAL4; TLDc; V-ATPase; mustard; oxidative stress; seizures; speech delay.
Copyright © 2019 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
W.B. and J.R. are employees of the Department of Molecular and Human Genetics at Baylor College of Medicine and Baylor Genetics Laboratories.
J.J. is an employee of GeneDx, Inc.
The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A loss-of-function mutation in human Oxidation Resistance 1 disrupts the spatial-temporal regulation of histone arginine methylation in neurodevelopment.Genome Biol. 2023 Sep 29;24(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-03037-1. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 37773136 Free PMC article.
-
The evolutionary conserved TLDc domain defines a new class of (H+)V-ATPase interacting proteins.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 22;11(1):22654. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01809-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34811399 Free PMC article.
-
The Evolutionarily Conserved Tre2/Bub2/Cdc16 (TBC), Lysin Motif (LysM), Domain Catalytic (TLDc) Domain Is Neuroprotective against Oxidative Stress.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 5;291(6):2751-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.685222. Epub 2015 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26668325 Free PMC article.
-
Preventing Neurodegeneration by Controlling Oxidative Stress: The Role of OXR1.Front Neurosci. 2020 Dec 15;14:611904. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.611904. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33384581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebellar atrophy in genetic epileptic encephalopathies: A cohort study and a systematic review.Seizure. 2024 Aug;120:41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2024.06.013. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Seizure. 2024. PMID: 38897163
Cited by
-
Knockout of the V-ATPase interacting protein Tldc2 in B-type kidney intercalated cells impairs urine alkalinization.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025 Jun 1;328(6):F890-F906. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00363.2024. Epub 2025 May 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40358928 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-668-3p regulates oxidative stress and cell damage induced by Aβ1-42 by targeting the OXR1/p53-p21 axis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Sep;10(17):928. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3598. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36172098 Free PMC article.
-
The risks of using unapproved gene symbols.Am J Hum Genet. 2021 Oct 7;108(10):1813-1816. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.09.004. Am J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 34626580 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease protective allele of Clusterin modulates neuronal excitability through lipid-droplet-mediated neuron-glia communication.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 15:2024.08.14.24312009. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.14.24312009. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Mol Neurodegener. 2025 May 3;20(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00840-1. PMID: 39185522 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
TBC1D24 interacts with the v-ATPase and regulates intraorganellar pH in neurons.iScience. 2024 Dec 1;28(1):111515. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111515. eCollection 2025 Jan 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39758816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Volkert M.R., Wang J.Y., Elliott N.A. A functional genomics approach to identify and characterize oxidation resistance genes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008;477:331–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

