Diffusion-weighted imaging of the breast-a consensus and mission statement from the EUSOBI International Breast Diffusion-Weighted Imaging working group
- PMID: 31786616
- PMCID: PMC7033067
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-019-06510-3
Diffusion-weighted imaging of the breast-a consensus and mission statement from the EUSOBI International Breast Diffusion-Weighted Imaging working group
Abstract
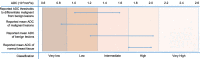
The European Society of Breast Radiology (EUSOBI) established an International Breast DWI working group. The working group consists of clinical breast MRI experts, MRI physicists, and representatives from large vendors of MRI equipment, invited based upon proven expertise in breast MRI and/or in particular breast DWI, representing 25 sites from 16 countries. The aims of the working group are (a) to promote the use of breast DWI into clinical practice by issuing consensus statements and initiate collaborative research where appropriate; (b) to define necessary standards and provide practical guidance for clinical application of breast DWI; (c) to develop a standardized and translatable multisite multivendor quality assurance protocol, especially for multisite research studies; (d) to find consensus on optimal methods for image processing/analysis, visualization, and interpretation; and (e) to work collaboratively with system vendors to improve breast DWI sequences. First consensus recommendations, presented in this paper, include acquisition parameters for standard breast DWI sequences including specifications of b values, fat saturation, spatial resolution, and repetition and echo times. To describe lesions in an objective way, levels of diffusion restriction/hindrance in the breast have been defined based on the published literature on breast DWI. The use of a small ROI placed on the darkest part of the lesion on the ADC map, avoiding necrotic, noisy or non-enhancing lesion voxels is currently recommended. The working group emphasizes the need for standardization and quality assurance before ADC thresholds are applied. The working group encourages further research in advanced diffusion techniques and tailored DWI strategies for specific indications. Key Points • The working group considers breast DWI an essential part of a multiparametric breast MRI protocol and encourages its use. • Basic requirements for routine clinical application of breast DWI are provided, including recommendations on b values, fat saturation, spatial resolution, and other sequence parameters. • Diffusion levels in breast lesions are defined based on meta-analysis data and methods to obtain a reliable ADC value are detailed.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Breast; Breast neoplasms; Consensus; Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies: Canon Medical systems, General Electric, Philips Healthcare, Siemens healthineers, Olea medical. Representatives of these companies were invited to participate as members in the working group, and had the opportunity to comment on the contents of the paper. The members of the scientific committee (who have no relationships to these companies) authorized eventual suggestions.
Figures

References
-
- Woodhams R, Matsunaga K, Iwabuchi K, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of malignant breast tumors: the usefulness of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value and ADC map for the detection of malignant breast tumors and evaluation of cancer extension. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2005;29:644–649. doi: 10.1097/01.rct.0000171913.74086.1b. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rubesova E, Grell AS, De Maertelaer V, Metens T, Chao SL, Lemort M (2006) Quantitative diffusion imaging in breast cancer: a clinical prospective study. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:319–324. 10.1002/jmri.20643 - PubMed
-
- Baltzer PAT, Renz DM, Herrmann K-H, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in MR mammography (MRM): clinical comparison of echo planar imaging (EPI) and half-Fourier single-shot turbo spin echo (HASTE) diffusion techniques. Eur Radiol. 2009;19:1612–1620. doi: 10.1007/s00330-009-1326-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

