Attenuation of Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension in BubR1 Low-Expression Mice Via Repression of Angiotensin II Receptor 1 Overexpression
- PMID: 31787052
- PMCID: PMC6912983
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011911
Attenuation of Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension in BubR1 Low-Expression Mice Via Repression of Angiotensin II Receptor 1 Overexpression
Abstract
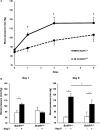
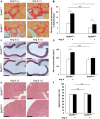
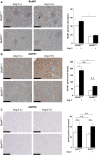
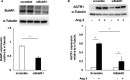
Background Angiotensin II (Ang II) can cause hypertension and tissue impairment via AGTR1 (Ang II receptor type 1), particularly in renal proximal tubule cells, and can cause DNA damage in renal cells via nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase. BubR1 (budding uninhibited by benzimidazole-related 1) is a multifaceted kinase that functions as a mitotic checkpoint. BubR1 expression can be induced by Ang II in smooth muscle cells in vitro, but the relationship between systemic BubR1 expression and the Ang II response is unclear. Methods and Results Twenty 24-week-old male BubR1 low-expression mice (BubR1L/L mice) and age-matched BubR1+/+ mice were used in this study. We investigated how Ang II stimulation affects BubR1L/L mice. The elevated systolic blood pressure caused by Ang II stimulation in BubR1+/+ mice was significantly attenuated in BubR1L/L mice. Additionally, an attenuated level of Ang II-induced perivascular fibrosis was observed in the kidneys of BubR1L/L mice. Immunohistochemistry revealed that the overexpression of AGTR1 induced by Ang II stimulation was repressed in BubR1L/L mice. We evaluated AGTR1 and Nox-4 (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-4) levels to determine the role of BubR1 in the Ang II response. Results from in vitro assays of renal proximal tubule cells suggest that treatment with small interfering RNA targeting BubR1 suppressed Ang II-induced overexpression of AGTR1. Similarly, the upregulation in Nox4 and Jun N-terminal kinase induced by Ang II administration was repressed by treatment with small interfering RNA targeting BubR1. Conclusions Ang II-induced hypertension is caused by AGTR1 overexpression in the kidneys via the upregulation of BubR1 and Nox4.
Keywords: angiotensin II type 1 receptor; budding uninhibited by benzimidazole‐related 1; hypertension; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase‐4; renal proximal tubule cell.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II upregulates LDL receptor-related protein (LRP1) expression in the vascular wall: a new pro-atherogenic mechanism of hypertension.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Jun 1;78(3):581-9. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn043. Epub 2008 Feb 15. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18281370
-
Angiotensin II receptor type 1-mediated vascular oxidative stress and proinflammatory gene expression in aldosterone-induced hypertension: the possible role of local renin-angiotensin system.Endocrinology. 2007 Apr;148(4):1688-96. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-1157. Epub 2007 Jan 11. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17218415
-
Adenoviral inhibition of AT1a receptors in the paraventricular nucleus inhibits acute increases in mean arterial blood pressure in the rat.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Nov;299(5):R1202-11. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00764.2009. Epub 2010 Aug 11. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20702798
-
Proximal Tubule-Specific Deletion of the NHE3 (Na+/H+ Exchanger 3) in the Kidney Attenuates Ang II (Angiotensin II)-Induced Hypertension in Mice.Hypertension. 2019 Sep;74(3):526-535. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13094. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 31352824 Free PMC article.
-
Role and therapeutic potential of G-protein coupled receptors in breast cancer progression and metastases.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Sep 15;763(Pt B):178-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.05.011. Epub 2015 May 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25981295 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated blood pressure in high-fat diet-exposed low birthweight rat offspring is most likely caused by elevated glucocorticoid levels due to abnormal pituitary negative feedback.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 27;15(8):e0238223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238223. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32853260 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress in Kidney Injury and Hypertension.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Nov 27;13(12):1454. doi: 10.3390/antiox13121454. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Insight on Multicentric Signaling of Angiotensin II in Cardiovascular system: A Recent Update.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 20;12:734917. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.734917. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34489714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cruickshank JM, Thorp JM, Zacharias FJ. Benefits and potential harm of lowering high blood pressure. Lancet. 1987;1:581–584. - PubMed
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. - PubMed
-
- MacMahon S, Peto R, Cutler J, Collins R, Sorlie P, Neaton J, Abbott R, Godwin J, Dyer A, Stamler J. Blood pressure, stroke, and coronary heart disease. Part 1, prolonged differences in blood pressure: prospective observational studies corrected for the regression dilution bias. Lancet. 1990;335:765–774. - PubMed
-
- de Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright JW, Unger T. International Union of Pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:415–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

