Characterization of the selective in vitro and in vivo binding properties of crenezumab to oligomeric Aβ
- PMID: 31787113
- PMCID: PMC6886224
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-019-0553-5
Characterization of the selective in vitro and in vivo binding properties of crenezumab to oligomeric Aβ
Abstract
Background: Accumulation of amyloid β (Aβ) in the brain is proposed as a cause of Alzheimer's disease (AD), with Aβ oligomers hypothesized to be the primary mediators of neurotoxicity. Crenezumab is a humanized immunoglobulin G4 monoclonal antibody that has been shown to bind to synthetic monomeric and aggregated Aβ in vitro; however, less is known about the binding characteristic in vivo. In this study, we evaluated the binding patterns of crenezumab to synthetic and native forms of Aβ both in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: Crenezumab was used to immunoprecipitate Aβ from synthetic Aβ preparations or brain homogenates from a PS2APP mouse model of AD to determine the forms of Aβ that crenezumab interacts with. Following systemic dosing in PS2APP or nontransgenic control mice, immunohistochemistry was used to localize crenezumab and assess its relative distribution in the brain, compared with amyloid plaques and markers of neuritic dystrophies (BACE1; LAMP1). Pharmacodynamic correlations were performed to investigate the relationship between peripheral and central target engagement.
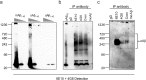
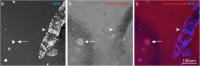
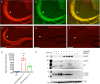
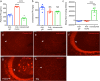
Results: In vitro, crenezumab immunoprecipitated Aβ oligomers from both synthetic Aβ preparations and endogenous brain homogenates from PS2APP mice. In vivo studies in the PS2APP mouse showed that crenezumab localizes to regions surrounding the periphery of amyloid plaques in addition to the hippocampal mossy fibers. These regions around the plaques are reported to be enriched in oligomeric Aβ, actively incorporate soluble Aβ, and contribute to Aβ-induced neurotoxicity and axonal dystrophy. In addition, crenezumab did not appear to bind to the dense core region of plaques or vascular amyloid.
Conclusions: Crenezumab binds to multiple forms of amyloid β (Aβ), particularly oligomeric forms, and localizes to brain areas rich in Aβ oligomers, including the halo around plaques and hippocampal mossy fibers, but not to vascular Aβ. These insights highlight a unique mechanism of action for crenezumab of engaging Aβ oligomers.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid β; Crenezumab; Mossy fiber; Oligomeric; Vascular amyloid.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are full-time employees of Genentech, Inc., and shareholders in F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Haass C, Selkoe DJ. Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: lessons from the Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Benilova I, Karran E, De Strooper B. The toxic Aβ oligomer and Alzheimer’s disease: an emperor in need of clothes. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:349–357. - PubMed
-
- Lesne S, Koh MT, Kotilinek L, Kayed R, Glabe CG, Yang A, et al. A specific amyloid-beta protein assembly in the brain impairs memory. Nature. 2006;440:352–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

