The SLC25 Mitochondrial Carrier Family: Structure and Mechanism
- PMID: 31787485
- PMCID: PMC7611774
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2019.11.001
The SLC25 Mitochondrial Carrier Family: Structure and Mechanism
Abstract
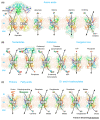
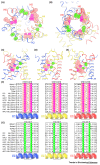
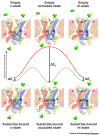
Members of the mitochondrial carrier family (SLC25) provide the transport steps for amino acids, carboxylic acids, fatty acids, cofactors, inorganic ions, and nucleotides across the mitochondrial inner membrane and are crucial for many cellular processes. Here, we use new insights into the transport mechanism of the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier to examine the structure and function of other mitochondrial carriers. They all have a single substrate-binding site and two gates, which are present on either side of the membrane and involve salt-bridge networks. Transport is likely to occur by a common mechanism, in which the coordinated movement of six structural elements leads to the alternating opening and closing of the matrix or cytoplasmic side of the carriers.
Keywords: adenine nucleotide translocase; energetics; mitochondrial transport; salt-bridge networks; transport mechanism; uncoupling protein.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Palmieri F, Klingenberg M. On the possible role of structural protein in the binding and translocation of adenine nucleotides in mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;131:582–585. - PubMed
-
- Aquila H, et al. Complete amino acid sequence of the ADP/ATP carrier from beef heart mitochondria. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1982;363:345–349. - PubMed
-
- Klingenberg M. The ADP and ATP transport in mitochondria and its carrier. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1778:1978–2021. - PubMed
-
- Kunji ERS, et al. The transport mechanism of the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863:2379–2393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

