Role of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK Signalling in cAMP/Epac-Mediated Endothelial Barrier Stabilisation
- PMID: 31787905
- PMCID: PMC6855264
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01387
Role of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK Signalling in cAMP/Epac-Mediated Endothelial Barrier Stabilisation
Abstract
Background and aims: Activation of the cAMP/Epac signalling stabilises endothelial barrier function. Moreover, its activation is accompanied by an activation of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK signalling in diverse cell types but their impact on endothelial barrier function is largely unknown. Here the role of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK signalling in cAMP/Epac-mediated endothelial barrier stabilisation was analysed.
Methods: Endothelial barrier function was analysed in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) by measuring flux of albumin. A modified cAMP analogue 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP (Epac agonist) was used to specifically activate cAMP/Epac signalling.
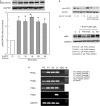
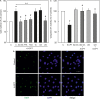
Results: Epac agonist reduces the basal and attenuates thrombin-induced endothelial hyperpermeability accompanied by an activation of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK signalling. The qPCR data demonstrate HUVECs express PI3Kα, PI3Kβ, and PI3Kγ but not PI3Kδ isoforms. The western blot data demonstrate Epac agonist activates PI3Kα and PI3Kβ isoforms. Inhibition of MEK/ERK but not PI3K/Akt pathway potentiates the endothelial barrier protective effects of cAMP/Epac signalling. Inhibition of MEK/ERK signalling in the presence of Epac agonist induces a reorganisation of actin cytoskeleton to the cell periphery, enhanced VE-cadherin localisation at cell-cell junctions, and dephosphorylation of myosin light chains (MLC) but not inhibition of RhoA/Rock signalling. Moreover, Epac agonist promotes endothelial cell (EC) survival via reduction in activities of pro-apoptotic caspases in a PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK signalling-dependent manner.
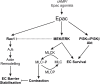
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate that the Epac agonist simultaneously activates diverse signalling pathways in ECs, which may have differential effects on endothelial barrier function. It activates PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK signalling which mainly govern its pro-survival effects on ECs. Inhibition of MEK/ERK but not PI3K/Akt signalling enhances barrier stabilising and barrier protective effects of cAMP/Epac activation.
Chemical compounds used in this study: 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP (PubChem CID: 9913268); Akt inhibitor VIII (PubChem CID: 10196499); AS-252424 (PubChem CID: 11630874); IC-87114 (PubChem CID: 9908783); PD 98059 (PubChem CID: 4713); PIK-75 (PubChem CID: 10275789); TGX-221 (PubChem CID: 9907093); Thrombin (PubChem CID: 90470996); U0126 (PubChem CID: 3006531); Wortmannin (PubChem CID: 312145).
Keywords: MEK/ERK; PI3K/Akt; Rac1; VE-cadherin; adherens junctions; cell survival; endothelial permeability; peripheral actin.
Copyright © 2019 Gündüz, Troidl, Tanislav, Rohrbach, Hamm and Aslam.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced endothelial barrier failure: role of RhoA, Rac1 and myosin light chain kinase.J Physiol. 2013 Jan 15;591(2):461-73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.237834. Epub 2012 Oct 22. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23090948 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP/PKA antagonizes thrombin-induced inactivation of endothelial myosin light chain phosphatase: role of CPI-17.Cardiovasc Res. 2010 Jul 15;87(2):375-84. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq065. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Cardiovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20202976
-
Intermedin (adrenomedullin2) stabilizes the endothelial barrier and antagonizes thrombin-induced barrier failure in endothelial cell monolayers.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;165(1):208-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01540.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21671901 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in obesity.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Mar;159:114244. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114244. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36638594 Review.
-
Cell physiology of cAMP sensor Epac.J Physiol. 2006 Nov 15;577(Pt 1):5-15. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.119644. Epub 2006 Sep 14. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16973695 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
BRAF Modulates the Interplay Between Cell-Cell and Cell-Extracellular Matrix Adhesions in PECAM-1-Mediated Mechanotransduction.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 18;25(20):11234. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011234. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457016 Free PMC article.
-
The Potentially Therapeutic Role of EPAC in Curbing the Process of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis via Differential Cellular Pathways.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Feb 26;14:611-619. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S296382. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 33679138 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol and its metabolites elicit neuroprotection via high-affinity binding to the laminin receptor at low nanomolar concentrations.FEBS Lett. 2024 May;598(9):995-1007. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14835. Epub 2024 Feb 27. FEBS Lett. 2024. PMID: 38413095 Free PMC article.
-
Methylglyoxal-Derived Nucleoside Adducts Drive Vascular Dysfunction in a RAGE-Dependent Manner.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;13(1):85. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010085. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247509 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives of PDE inhibitor on treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 14;14:1111393. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1111393. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36865908 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

