Anxiolytic Effects of Repeated Cannabidiol Treatment in Teenagers With Social Anxiety Disorders
- PMID: 31787910
- PMCID: PMC6856203
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02466
Anxiolytic Effects of Repeated Cannabidiol Treatment in Teenagers With Social Anxiety Disorders
Abstract
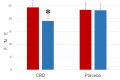
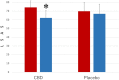
Accumulated evidence indicates that cannabidiol (CBD), a nonpsychotomimetic and nonaddictive main component of the Cannabis sativa plant, reverses anxiety-like behavior. The purpose of the present study was to assess the efficacy of CBD treatment for Japanese late teenagers with social anxiety disorder (SAD). Thirty-seven 18-19-year-old Japanese teenagers with SAD and avoidant personality disorder received, in a double-blind study, cannabis oil (n = 17) containing 300 mg CBD or placebo (n = 20) daily for 4 weeks. SAD symptoms were measured at the beginning and end of the treatment period using the Fear of Negative Evaluation Questionnaire and the Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale. CBD significantly decreased anxiety measured by both scales. The results indicate that CBD could be a useful option to treat social anxiety.
Keywords: avoidant personality disorder; cannabidiol; cannabinoid; cannabis; social anxiety disorder; social phobia; social withdrawal.
Copyright © 2019 Masataka.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cannabidiol reduces the anxiety induced by simulated public speaking in treatment-naïve social phobia patients.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011 May;36(6):1219-26. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.6. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21307846 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cannabidiol Treatment Shows Therapeutic Efficacy in a Rodent Model of Social Transfer of Pain in Pair-Housed Male Mice.Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2024 Jun;9(3):699-713. doi: 10.1089/can.2022.0300. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2024. PMID: 37074109
-
Cannabidiol treatment in an adolescent with multiple substance abuse, social anxiety and depression.Neuropsychiatr. 2021 Mar;35(1):31-34. doi: 10.1007/s40211-020-00334-0. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Neuropsychiatr. 2021. PMID: 32052321 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabidiol, a Cannabis sativa constituent, as an anxiolytic drug.Braz J Psychiatry. 2012 Jun;34 Suppl 1:S104-10. doi: 10.1590/s1516-44462012000500008. Braz J Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22729452 Review. English, Portuguese.
-
Cannabidiol, a Cannabis sativa constituent, as an antipsychotic drug.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2006 Apr;39(4):421-9. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2006000400001. Epub 2006 Apr 3. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2006. PMID: 16612464 Review.
Cited by
-
Selected Seeds as Sources of Bioactive Compounds with Diverse Biological Activities.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 30;15(1):187. doi: 10.3390/nu15010187. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36615843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabidiol (CBD) in Rheumatic Diseases (Musculoskeletal Pain).Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2022 Jul;24(7):238-246. doi: 10.1007/s11926-022-01077-3. Epub 2022 May 3. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35503198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medicinal Cannabis for Paediatric Developmental, Behavioural and Mental Health Disorders.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Apr 7;20(8):5430. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20085430. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37107712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expectancies of the Effects of Cannabis Use in Individuals with Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD).Brain Sci. 2024 Mar 2;14(3):246. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14030246. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38539634 Free PMC article.
-
Motivations for Cannabis Use in Individuals with Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD).Brain Sci. 2023 Dec 9;13(12):1698. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13121698. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 38137146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th Edn. (Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, Text Revision; ), 1–302.
-
- Antony M. M., Rowa K. (2008). Social anxiety disorder. (Cambridge, MA: Hogrefe; ), 1–177.
-
- Bergamaschi M. M., Queiroz R. H. C., Chagas M. H. N., de Oliveira D. C. G., De Martinis B. S., Kapczinski F., et al. (2011). Cannabidiol reduces the anxiety induced by simulated public speaking in treatment-naïve social phobia patients. Neuropsychopharmcology 36, 1219–1226. 10.1038/npp.2011.6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

