Comparative Evaluation of Different Sanitizers Against Listeria monocytogenes Biofilms on Major Food-Contact Surfaces
- PMID: 31787935
- PMCID: PMC6853887
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02462
Comparative Evaluation of Different Sanitizers Against Listeria monocytogenes Biofilms on Major Food-Contact Surfaces
Abstract
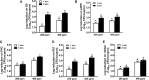
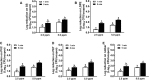
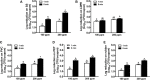
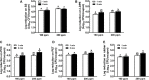
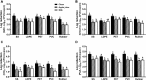
Contaminated food-contact surfaces are recognized as the primary reason for recent L. monocytogenes outbreaks in caramel apples and cantaloupes, highlighting the significance of cleaning and sanitizing food-contact surfaces to ensure microbial safety of fresh produce. This study evaluated efficacies of four commonly used chemical sanitizers at practical concentrations against L. monocytogenes biofilms on major food-contact surfaces including stainless steel, low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyester (PET), and rubber. In general, efficacies against L. monocytogenes biofilms were enhanced by increasing concentrations of quaternary ammonium compound (QAC), chlorine, and chlorine dioxide, or extending treating time from 1 to 5 min. The 5-min treatments of 400 ppm QAC, 5.0 ppm chlorine dioxide, and 200 ppm chlorine reduced 3.0-3.7, 2.4-2.7, and 2.6-3.8 log10 CFU/coupon L. monocytogenes biofilms depending on surfaces. Peroxyacetic acid (PAA) at 160 and 200 ppm showed similar antimicrobial efficacies against biofilms either at 1- or 5-min contact. The 5-min treatment of 200 ppm PAA caused 4.0-4.5 log10 CFU/coupon reduction of L. monocytogenes biofilms on tested surfaces. Surface material had more impact on the efficacies of QAC and chlorine, less influence on those of PAA and chlorine dioxide, while organic matter soiling impaired sanitizer efficacies against L. monocytogenes biofilms independent of food-contact surfaces. Data from this study provide practical guidance for effective disinfection of food-contact surfaces in food processing/packing facilities.
Keywords: L. monocytogenes; biofilm; food-contact surfaces; organic matter; peroxyacetic acid; sanitizers.
Copyright © 2019 Hua, Korany, El-Shinawy and Zhu.
Figures
References
-
- Aarnisalo K., Salo S., Miettinen H., Suihko M. L., Wirtanen G., Autio T., et al. (2000). Bactericidal efficiencies of commercial disinfectants against Listeria monocytogenes on surfaces. J. Food Saf. 20, 237–250. 10.1111/j.1745-4565.2000.tb00302.x - DOI
-
- Abeysundara P. D. A., Dhowlaghar N., Nannapaneni R., Schilling M. W., Mahmoud B., Sharma C. S., et al. (2018). Salmonella enterica growth and biofilm formation in flesh and peel cantaloupe extracts on four food-contact surfaces. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 280, 17–26. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.04.042, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Angelo K. M., Conrad A. R., Saupe A., Dragoo H., West N., Sorenson A., et al. (2017). Multistate outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes infections linked to whole apples used in commercially produced, prepackaged caramel apples: United States, 2014-2015. Epidemiol. Infect. 145, 848–856. 10.1017/S0950268816003083 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

