The effect of western diet on mice brain lipid composition
- PMID: 31788013
- PMCID: PMC6880556
- DOI: 10.1186/s12986-019-0401-4
The effect of western diet on mice brain lipid composition
Erratum in
-
Correction to: The effect of western diet on mice brain lipid composition.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020 Apr 16;17:30. doi: 10.1186/s12986-020-00444-0. eCollection 2020. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32322288 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The appropriate fatty acids composition of brain lipids is critical for functioning of this organ. The alterations of brain fatty acids composition may lead to neurological and neurodegenerative diseases.
Methods: The aim of this work was to evaluate the effect of western diet containing high fat content on fatty acid composition of brain lipids. In this study we used mice fed high fat diet (HFD) for 19 weeks. Brain lipids were separated by SPE extraction and fatty acid composition in chow, mice serum, brain and other tissues was analyzed by GC-MS method.
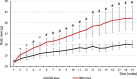
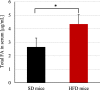
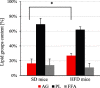
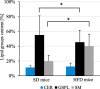
Results: The body weight and adipose tissue weigh of mice after HFD increased significantly. The concentrations of most of fatty acids in serum of mice after HFD increased, due to their higher delivery from food. Unexpectedly the serum eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) concentration was lower in mice after HFD than in controls. Also the brain, and other tissue EPA content was lower. Among studied groups of brain lipids EPA was significantly decreased in phospholipids and sphingolipids.
Conclusions: Considering important role of brain EPA including maintaining of appropriate composition of cell membrane lipids and anti-inflammatory properties we conclude that decrease of brain EPA after western diet may result in impaired brain function.
Keywords: Docosahexaenoic acid; Eicosapentaenoic acid; High-fat diet; Mice model; Phospholipids; Polyunsaturated fatty acids; Sphingolipids; brain; obesity.
© The Author(s). 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effect of a High-Fat Diet on the Fatty Acid Composition in the Hearts of Mice.Nutrients. 2020 Mar 20;12(3):824. doi: 10.3390/nu12030824. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32245049 Free PMC article.
-
The Omega-3 Fatty Acids EPA and DHA, as a Part of a Murine High-Fat Diet, Reduced Lipid Accumulation in Brown and White Adipose Tissues.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 24;20(23):5895. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235895. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31771283 Free PMC article.
-
Eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acid-enriched high fat diet delays the development of fatty liver in mice.Lipids Health Dis. 2015 Jul 22;14:74. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0072-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2015. PMID: 26193881 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary DHA/EPA Ratio Changes Fatty Acid Composition and Attenuates Diet-Induced Accumulation of Lipid in the Liver of ApoE-/- Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Nov 14;2018:6256802. doi: 10.1155/2018/6256802. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30538803 Free PMC article.
-
Fish oil supplementation alleviates metabolic and anxiodepressive effects of diet-induced obesity and associated changes in brain lipid composition in mice.Int J Obes (Lond). 2020 Sep;44(9):1936-1945. doi: 10.1038/s41366-020-0623-6. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Int J Obes (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32546855
Cited by
-
The Effect of a High-Fat Diet on the Fatty Acid Composition in the Hearts of Mice.Nutrients. 2020 Mar 20;12(3):824. doi: 10.3390/nu12030824. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32245049 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial Lipid Biology in the Hypothalamic Regulation of Metabolic Homeostasis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 May 27;12:668396. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.668396. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34122343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correction to: The effect of western diet on mice brain lipid composition.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020 Apr 16;17:30. doi: 10.1186/s12986-020-00444-0. eCollection 2020. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32322288 Free PMC article.
-
Early Life to Adult Brain Lipidome Dynamic: A Temporospatial Study Investigating Dietary Polar Lipid Supplementation Efficacy.Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 26;9:898655. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.898655. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35967787 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitate and thapsigargin have contrasting effects on ER membrane lipid composition and ER proteostasis in neuronal cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2022 Nov;1867(11):159219. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2022.159219. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2022. PMID: 35981704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- USDA . Profiling Food Consumption in America. Agric Fact B. Washington D.C.: Office of Communications, U.S. Dept. of Agriculture; 2001. pp. 13–22.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

