Cytochrome C inhibits tumor growth and predicts favorable prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 31788077
- PMCID: PMC6866253
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10989
Cytochrome C inhibits tumor growth and predicts favorable prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
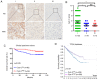
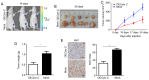
Cytochrome C (Cyto C), a multifunctional enzyme, has been demonstrated to be associated with cell apoptosis and respiration. Accumulating evidence has revealed that serum Cyto C is an effective indicator in evaluating the effect of chemotherapy. However, to the best of our knowledge, the clinical significance of Cyto C and its role in cell growth and apoptosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) remain unknown. In the present study, Cyto C expression was detected in 150 CCRCC and 30 normal tissues samples via immunohistochemistry. The results demonstrated that Cyto C protein expression levels in CCRCC tissues were downregulated compared with those in corresponding normal tissues. In addition, it was revealed that Cyto C expression was negatively associated with TNM stage. Further analyses revealed that patients with CCRCC and low Cyto C expression levels had a shorter survival time than those with high Cyto C expression. Multivariate analyses indicated that high Cyto C expression levels were an independent prognostic factor for survival. Functionally, overexpression of Cyto C effectively suppressed the growth of CCRCC cells and induced cell apoptosis, and knockdown of Cyto C reversed these effects. Finally, overexpression of Cyto C inhibited the tumor growth of CCRCC cells in vivo. Overall, the data of the present study indicated that Cyto C may be a novel prognostic biomarker and acted as a regulator of tumor growth in CCRCC.
Keywords: apoptosis; clear renal cell carcinoma; cytochrome C; proliferation.
Copyright: © Liu et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long Non-Coding RNA LUCAT1 Promotes Proliferation and Invasion in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Through AKT/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(3):891-904. doi: 10.1159/000491957. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30032137
-
DKC1 serves as a potential prognostic biomarker for human clear cell renal cell carcinoma and promotes its proliferation, migration and invasion via the NF‑κB pathway.Oncol Rep. 2018 Aug;40(2):968-978. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6484. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29901172
-
Golgi Alpha-Mannosidase II as a Novel Biomarker Predicts Prognosis in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Oncol Res Treat. 2020;43(6):264-275. doi: 10.1159/000505931. Epub 2020 May 13. Oncol Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32403105
-
PinX1 serves as a potential prognostic indicator for clear cell renal cell carcinoma and inhibits its invasion and metastasis by suppressing MMP-2 via NF-κB-dependent transcription.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 28;6(25):21406-20. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4011. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26033551 Free PMC article.
-
High kinesin family member 11 expression predicts poor prognosis in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.J Clin Pathol. 2019 May;72(5):354-362. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2018-205390. Epub 2019 Feb 28. J Clin Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30819726 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cytochrome c in cancer therapy and prognosis.Biosci Rep. 2022 Dec 22;42(12):BSR20222171. doi: 10.1042/BSR20222171. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36479932 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of apigenin and chemotherapy combination treatments on apoptosis-related genes and proteins in acute leukaemia cell lines.Sci Rep. 2022 May 25;12(1):8858. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11441-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35614109 Free PMC article.
-
A new nano approach to prevent tumor growth in the local treatment of glioblastoma: Temozolomide and rutin-loaded hybrid layered composite nanofiber.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2024 Dec;19(6):100971. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2024.100971. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39640055 Free PMC article.
-
Double face of cytochrome c in cancers by Raman imaging.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 8;12(1):2120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-04803-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35136078 Free PMC article.
-
Pomegranate Peel Phytochemistry, Pharmacological Properties, Methods of Extraction, and Its Application: A Comprehensive Review.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 19;8(39):35452-35469. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02586. eCollection 2023 Oct 3. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37810640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mijuskovic M, Stanojevic I, Milovic N, Cerovic S, Petrovic D, Maksic D, Kovacevic B, Andjelic T, Aleksic P, Terzic B, et al. Tissue and urinary KIM-1 relate to tumor characteristics in patients with clear renal cell carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018;50:63–70. doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1724-6. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
