Anterior Cortical Window Technique Instead of Extended Trochanteric Osteotomy in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Minimum 10-Year Follow-up
- PMID: 31788161
- PMCID: PMC6867915
- DOI: 10.4055/cios.2019.11.4.396
Anterior Cortical Window Technique Instead of Extended Trochanteric Osteotomy in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Minimum 10-Year Follow-up
Abstract
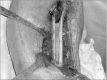
Background: The anterior cortical window technique was developed to facilitate stem removal in revision total hip arthroplasty (THA). In this technique, only the anterior cortex of the proximal femur is osteomized; the trochanter, lateral cortex, and medial cortex remain intact. Therefore, a new stem can be press-fitted into the femur and mediolateral stability can be obtained. However, the long-term results of revision THA using this technique are unknown. We report the outcome and survivorship at a minimum of 10-year follow-up.
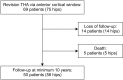
Methods: From May 2003 to April 2006, 69 patients (75 hips) underwent revision THA using an anterior cortical window and a cementless distal interlocking stem. Of these, 50 patients (56 hips) were followed up for 10 to 13 years (mean, 11.5 years). There were 26 men (29 hips) and 24 women (27 hips) with a mean age of 51.2 years (range, 29 to 82 years) at the time of revision arthroplasty. We evaluated radiographs, Harris hip score, University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) activity score, Koval category, and survivorship.
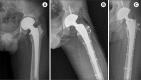
Results: Nonunion of the osteotomy occurred in one hip (2%). Five stems (8.9%) subsided 5 mm or more. At the final evaluation, the mean Harris hip score, UCLA activity score, and the Koval category were 82.5, 4.6, and 1.5, respectively. Survivorship with any operations as the end point was 80.4% and that with stem-revision as the end point was 91.1%.
Conclusions: With use of an anterior cortical window, a well-fixed stem can be easily removed, and a new stem can be inserted with firm mediolateral stability in the proximal femur in revision THA. We recommend using this technique instead of the extended trochanteric osteotomy in revision THA.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Hip; Reoperation; Replacement; Survival rate.
Copyright © 2019 by The Korean Orthopaedic Association.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Kurtz S, Mowat F, Ong K, Chan N, Lau E, Halpern M. Prevalence of primary and revision total hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 1990 through 2002. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(7):1487–1497. - PubMed
-
- Patel A, Pavlou G, Mujica-Mota RE, Toms AD. The epidemiology of revision total knee and hip arthroplasty in England and Wales: a comparative analysis with projections for the United States. A study using the National Joint Registry dataset. Bone Joint J. 2015;97(8):1076–1081. - PubMed
-
- Younger TI, Bradford MS, Magnus RE, Paprosky WG. Extended proximal femoral osteotomy: a new technique for femoral revision arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1995;10(3):329–338. - PubMed
-
- Chen WM, McAuley JP, Engh CA, Jr, Hopper RH, Jr, Engh CA. Extended slide trochanteric osteotomy for revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(9):1215–1219. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

