The Consortium for the early identification of Alzheimer's disease-Quebec (CIMA-Q)
- PMID: 31788534
- PMCID: PMC6880140
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dadm.2019.07.003
The Consortium for the early identification of Alzheimer's disease-Quebec (CIMA-Q)
Abstract
Introduction: The Consortium for the early identification of Alzheimer's disease-Quebec (CIMA-Q) created a research infrastructure to recruit, characterize, and track disease progression in individuals at risk of dementia.
Methods: CIMA-Q established standardized clinical, neuropsychological, neuroimaging, blood (plasma, serum, RNA, genomic DNA), cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and cerebrospinal fluid collection protocols. These data and biological materials are available to the research community.
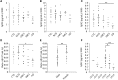
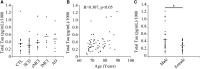
Results: In phase 1, 115 persons with subjective cognitive decline, 88 with mild cognitive impairment, 31 with early probable Alzheimer's disease, and 56 older adults with no worries nor impairments received detailed clinical and cognitive evaluations as well as blood and peripheral blood mononuclear cells collections. Among them, 142 underwent magnetic resonance imaging, 29 a 18fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography, and 60 a lumbar puncture.
Discussion: CIMA-Q provides procedures and resources to identify early biomarkers and novel therapeutic targets, and holds promise for detecting cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Biomarker; CIMA-Q; Clinical cohort; Consortium for the early identification of Alzheimer's disease-Quebec; Cryopreserved PBMNC; Early diagnosis; Mild cognitive impairment; Subjective cognitive decline.
© 2019 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Albert M.S., DeKosky S.T., Dickson D., Dubois B., Feldman H.H., Fox N.C. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's Dement. 2011;7:270–279. - PMC - PubMed
-
- McKhann G.M., Knopman D.S., Chertkow H., Hyman B.T., Jack C.R., Jr., Kawas C.H. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's Dement. 2011;7:263–269. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J., Csernansky J.G., Davatzikos C., Fox N.C., Frisoni G.B., Thompson P.M. Computer-assisted imaging to assess brain structure in healthy and diseased brains. Lancet Neurol. 2003;2:79–88. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
