Diagnostic approach of eosinophilic spongiosis
- PMID: 31789265
- PMCID: PMC6939072
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abd.2019.02.002
Diagnostic approach of eosinophilic spongiosis
Abstract
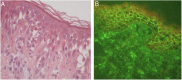
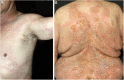
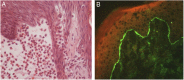
Eosinophilic spongiosis is a histological feature shared by some distinct inflammatory disorders, and is characterized by the presence of intraepidermal eosinophils associated with spongiosis. Most often, isolated eosinophilic spongiosis indicates the early stages of a subjacent autoimmune bullous dermatosis, such as the pemphigus group and bullous pemphigoid. Herein, the main causes of eosinophilic spongiosis are discussed, as well as the supplementary investigation needed to elucidate its etiology.
Keywords: Diagnosis, differential; Eosinophils; Pemphigoid, bullous; Pemphigus; Skin diseases, vesiculobullous.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U.
Figures


References
-
- Lepelletier C., Vignon-Pennamen M.D., Battistella M. Eosinophilic spongiosis. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2018;145:68–71. - PubMed
-
- Emmerson R.W., Wilson-Jones E. Eosinophilic spongiosis in pemphigus. A report of an unusual histological change in pemphigus. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:252–257. - PubMed
-
- Santi C.G., Maruta C.W., Aoki V., Sotto M.N., Rivitti E.A., Diaz L.A. Pemphigus herpetiformis is a rare clinical expression of nonendemic pemphigus foliaceus, fogo selvagem, and pemphigus vulgaris. Cooperative Group on Fogo Selvagem Research. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:40–46. - PubMed
-
- Laws P.M., Heelan K., Al-Mohammedi F., Walsh S., Shear N.H. Pemphigus herpetiformis: a case series and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2015;54:1014–1022. - PubMed
-
- Gallo E., García-Martín P., Fraga J., Teye K., Koga H., Hashimoto T. Paraneoplastic pemphigus with eosinophilic spongiosis and autoantibodies against desmocollins 2 and 3. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014;39:323–326. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

