Morphological, structural and physiological differences in heteromorphic leaves of Euphrates poplar during development stages and at crown scales
- PMID: 31793152
- PMCID: PMC7318281
- DOI: 10.1111/plb.13078
Morphological, structural and physiological differences in heteromorphic leaves of Euphrates poplar during development stages and at crown scales
Abstract
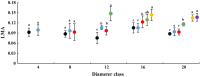
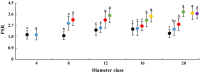
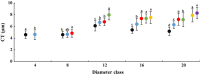
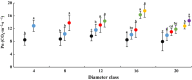
Euphrates poplar (Populus euphratica Oliv.) has heteromorphic leaves including strip, lanceolate, ovate, and broad-ovate leaves from base to top in the mature canopy. To clarify how diameter at breast height (DBH) and tree height affect the functional characteristics of all kinds of heteromorphic leaves, we measured the morphological anatomical structure and physiological indices of five crown heteromorphic leaves of P. euphratica at 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 m from the same site. We also analysed the relationships between morphological structures and physiological characteristics of heteromorphic leaves and DBH and the height of heteromorphic leaves. The results showed that the number of abnormalities regarding blade width, leaf area, leaf thickness, leaf mass per area, cuticle layer thickness, palisade tissue thickness, and palisade tissue/sponge tissue ratio increased with size order and sampling height gradient. Net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance, instantaneous water use efficiency, stable delta carbon isotope ratio, proline and malondialdehyde (MDA) content increased with DBH and sampling height. By contrast, blade length, leaf shape index, and intercellular CO2 concentration decreased with the increase in path order and sampling height gradient. Although MDA content and leaf sponge thickness were not correlated with DBH or sampling height, other morphological structure and physiological parameters were significantly correlated with these variables. In addition, correlations were found among leaf morphology, anatomical structure, and physiological index parameters indicating that they changed with path order and tree height gradient. The differences in the morphology, anatomic structure and physiological characteristics of the heteromorphic leaves ofP. euphratica are related to ontogenesis stage and coronal position.
Keywords: Heteromorphic leaf; Populus euphratica Oliv; morphological anatomy; osmotic regulation; photosynthetic water physiology.
© 2019 The Authors. Plant Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of German Society for Plant Sciences, Royal Botanical Society of the Netherlands.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural and Functional Responses of the Heteromorphic Leaves of Different Tree Heights on Populus euphratica Oliv. to Different Soil Moisture Conditions.Plants (Basel). 2022 Sep 12;11(18):2376. doi: 10.3390/plants11182376. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145777 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in studying heteromorphic leaves in Populus euphratica: leaf morphology, anatomical structure, development regulation and their ecological adaptation to arid environments.Plant Signal Behav. 2021 Apr 3;16(4):1870842. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2020.1870842. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Plant Signal Behav. 2021. PMID: 33427562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conjoint Analysis of Genome-Wide lncRNA and mRNA Expression of Heteromorphic Leavesin Response to Environmental Heterogeneityin Populus euphratica.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 17;20(20):5148. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205148. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31627402 Free PMC article.
-
iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis of heteromorphic leaves reveals eco-adaptability of Populus euphratica Oliv.J Plant Physiol. 2022 Apr;271:153644. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2022.153644. Epub 2022 Feb 10. J Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35219031
-
Current Advances in Molecular Basis and Mechanisms Regulating Leaf Morphology in Rice.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Oct 23;9:1528. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01528. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30405666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Architecture of Heterophylly: Single and Multi-Leaf Genome-Wide Association Mapping in Populus euphratica.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 15;13:870876. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.870876. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35783952 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of DNA Methyltransferase and Demethylase in Populus sect. Turanga and Their Potential Roles in Heteromorphic Leaf Development in Populus euphratica.Plants (Basel). 2025 Aug 1;14(15):2370. doi: 10.3390/plants14152370. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805719 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in the Functional Traits of Populus pruinosa Leaves in Different Developmental Stages.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jun 9;12(12):2262. doi: 10.3390/plants12122262. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375887 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological, Anatomical, and Physiological Characteristics of Heteroblastic Acacia melanoxylon Grown under Weak Light.Plants (Basel). 2024 Mar 18;13(6):870. doi: 10.3390/plants13060870. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38592868 Free PMC article.
-
Hydraulic constraints determine the distribution of heteromorphic leaves along plant vertical height.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 29;13:941764. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.941764. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36275510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apel K., Hirt H. (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 55, 373–399. - PubMed
-
- Bai S.N. (2003) Plant Developmental Biology. Beijing University Press, Beijing, China, pp 72–73.
-
- Bai X., Zhang S.J., Zheng C.X., Hao J.Q., Li W.H., Yang Y. (2011) Comparative study on photosynthesis and water physiology of polymorphic leaves of Populus euphratica . Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 33, 47–52.
-
- Chen Y.M., Chen H.B., Chen G.J., Wu Y.Y. (2001) A study on leaf structure and drought resistance of Banana. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 92, 14–16.
-
- England J.R., Attiwill M.P. (2006) Changes in leaf morphology and anatomy with tree age and height in the broadleaved evergreen species, Eucalyptus regnans F. Muell. Trees, 20, 79–90.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

