Electrochemical Access to Aza-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Rhoda-Electrocatalyzed Domino Alkyne Annulations
- PMID: 31793169
- PMCID: PMC7155118
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201914775
Electrochemical Access to Aza-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Rhoda-Electrocatalyzed Domino Alkyne Annulations
Abstract
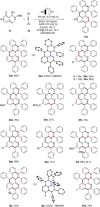
Nitrogen-doped polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (aza-PAHs) have found broad applications in material sciences. Herein, a modular electrochemical synthesis of aza-PAHs was developed via a rhodium-catalyzed cascade C-H activation and alkyne annulation. A multifunctional O-methylamidoxime enabled the high chemo- and regioselectivity. The isolation of two key rhodacyclic intermediates made it possible to delineate the exact order of three C-H activation steps. In addition, the metalla-electrocatalyzed multiple C-H transformation is characterized by unique functional group tolerance, including highly reactive iodo and azido groups.
Keywords: C−H activation; aza-PAHs; domino reactions; metalla-electrocatalysis; rhodium catalysis.
© 2019 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Rhodaelectrocatalysis for Annulative C-H Activation: Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons through Versatile Double Electrocatalysis.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 May 6;58(19):6342-6346. doi: 10.1002/anie.201901565. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 30835907
-
Metalla-electrocatalyzed C-H Activation by Earth-Abundant 3d Metals and Beyond.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Jan 21;53(1):84-104. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00510. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 31854967
-
Synthesis of Phenalenyl-Fused Pyrylium Cations: Divergent C-H Activation/Annulation Reaction Sequence of Naphthalene Aldehydes with Alkynes.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017 Oct 9;56(42):13094-13098. doi: 10.1002/anie.201708127. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017. PMID: 28834077
-
Transition Metal-Catalyzed Dual C-H Activation/Annulation Reactions Involving Internal Alkynes.Chem Rec. 2024 Jul;24(7):e202400069. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202400069. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Chem Rec. 2024. PMID: 38984737 Review.
-
Metallaelectro-catalyzed alkyne annulations via C-H activations for sustainable heterocycle syntheses.Chem Commun (Camb). 2024 Oct 22;60(85):12333-12364. doi: 10.1039/d4cc03871a. Chem Commun (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39370984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid access to polycyclic N-heteroarenes from unactivated, simple azines via a base-promoted Minisci-type annulation.Nat Commun. 2022 May 3;13(1):2421. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30086-0. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35504905 Free PMC article.
-
Computational, Mechanistic, and Experimental Insights into Regioselective Catalytic C-C Bond Activation in Linear 1-Aza-[3]triphenylene.ACS Omega. 2022 Mar 4;7(10):8665-8674. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c06664. eCollection 2022 Mar 15. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35309457 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodaelectro-Catalyzed peri-Selective Direct Alkenylations with Weak O-Coordination Enabled by the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER).Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 May 9;61(20):e202117188. doi: 10.1002/anie.202117188. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022. PMID: 35179817 Free PMC article.
-
Enantioselective Pallada-Electrocatalyzed C-H Activation by Transient Directing Groups: Expedient Access to Helicenes.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Aug 3;59(32):13451-13457. doi: 10.1002/anie.202003826. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32243685 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent rhodium-catalyzed electrochemical vinylic C-H annulation of acrylamides with alkynes.Nat Commun. 2021 Feb 10;12(1):930. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21190-8. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33568643 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

